Page 346 - Global Tectonics
P. 346
(a) Crust and marker grid
600 km India Suture Eurasia 1400 km
-1 0 1 2
0 UC
km 25 LC
35
V P = 20 mm a 1 S
(b) .
Temperature and velocity Denudation rate e = slope x f(t) x g(x) T s = 0 q s = 71.25 mW m –2
0
km 25 S A 1 A2
35 θ Moho = 704 o C
V P = 20 mm a 1 Initial conductive steady-state Retro-mantle
Lithosphere
Pro-mantle
Lithosphere q m = 20 mW m -2
0 km 200 Kinematic subduction
V:H = 1:1 V P = 20 mm a -1
(c) t = 30 Myr Δx = 1500 km Erosion front Current rate of erosion
Deformation 10 mm a 1 –2 –1 Suture
0
–7 –6 –5 –4 –3
V = 50 mm a 1 S
P
Velocity, temperature and radioactive heat sources V = 25 mm a –1
S
A = 2.0 μW m –3
1
o
700 C A = 0.75 μW m –3
o
V P = 50 mm a 1 800 C 2
(d) t = 39 Myr Δx = 1950 km Moho
10 mm a 1 S (Δx = 750 km)
–8 –7 –3 –2 –1 0 1
o
700 C
o
800 C
(e) t = 48 Myr Δx = 2400 km S (Δx = 975 km)
10 mm a 1
–9 –2 –1 0 1 2
o
700 C
o
800 C
0 km 200 S (Δx = 1200 km)
V:H = 1:1
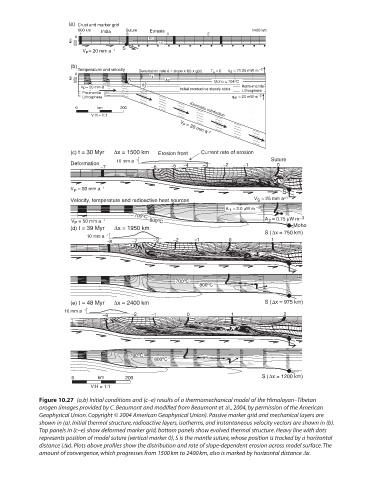
Figure 10.27 (a,b) Initial conditions and (c–e) results of a thermomechanical model of the Himalayan–Tibetan
orogen (images provided by C. Beaumont and modified from Beaumont et al., 2004, by permission of the American
Geophysical Union. Copyright © 2004 American Geophysical Union). Passive marker grid and mechanical layers are
shown in (a). Initial thermal structure, radioactive layers, isotherms, and instantaneous velocity vectors are shown in (b).
Top panels in (c–e) show deformed marker grid, bottom panels show evolved thermal structure. Heavy line with dots
represents position of model suture (vertical marker 0), S is the mantle suture, whose position is tracked by a horizontal
distance (Dx). Plots above profiles show the distribution and rate of slope-dependent erosion across model surface. The
amount of convergence, which progresses from 1500 km to 2400 km, also is marked by horizontal distance Dx.