Page 274 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 274
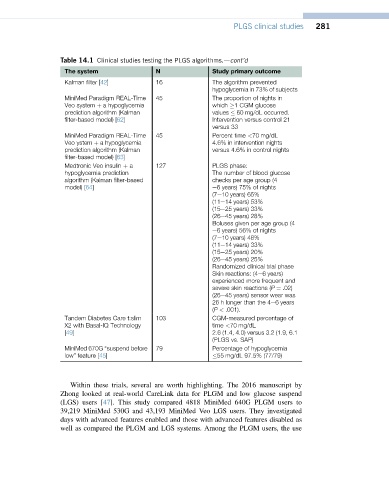
PLGS clinical studies 281
Table 14.1 Clinical studies testing the PLGS algorithms.dcont’d
The system N Study primary outcome
Kalman filter [42] 16 The algorithm prevented
hypoglycemia in 73% of subjects
MiniMed Paradigm REAL-Time 45 The proportion of nights in
Veo system þ a hypoglycemia which 1 CGM glucose
prediction algorithm (Kalman values 60 mg/dL occurred.
filter-based model) [62] Intervention versus control 21
versus 33
MiniMed Paradigm REAL-Time 45 Percent time <70 mg/dL
Veo ystem þ a hypoglycemia 4.6% in intervention nights
prediction algorithm (Kalman versus 4.6% in control nights
filter-based model) [63]
Medtronic Veo insulin þ a 127 PLGS phase:
hypoglycemia prediction The number of blood glucose
algorithm (Kalman filter-based checks per age group (4
model) [64] e6 years) 75% of nights
(7e10 years) 65%
(11e14 years) 53%
(15e25 years) 33%
(26e45 years) 28%
Boluses given per age group (4
e6 years) 56% of nights
(7e10 years) 48%
(11e14 years) 33%
(15e25 years) 20%
(26e45 years) 25%
Randomized clinical trial phase
Skin reactions: (4e6 years)
experienced more frequent and
severe skin reactions (P ¼ .02)
(26e45 years) sensor wear was
26 h longer than the 4e6 years
(P < .001).
Tandem Diabetes Care t:slim 103 CGM-measured percentage of
X2 with Basal-IQ Technology time <70 mg/dL
[49] 2.6 (1.4, 4.0) versus 3.2 (1.9, 6.1
(PLGS vs. SAP)
MiniMed 670G “suspend before 79 Percentage of hypoglycemia
low” feature [45] 55 mg/dL 97.5% (77/79)
Within these trials, several are worth highlighting. The 2016 manuscript by
Zhong looked at real-world CareLink data for PLGM and low glucose suspend
(LGS) users [47]. This study compared 4818 MiniMed 640G PLGM users to
39,219 MiniMed 530G and 43,193 MiniMed Veo LGS users. They investigated
days with advanced features enabled and those with advanced features disabled as
well as compared the PLGM and LGS systems. Among the PLGM users, the use