Page 273 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 273
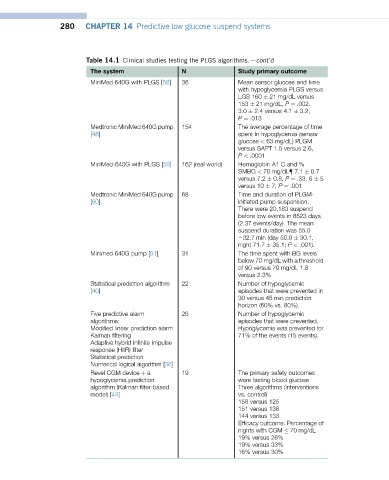
280 CHAPTER 14 Predictive low glucose suspend systems
Table 14.1 Clinical studies testing the PLGS algorithms.dcont’d
The system N Study primary outcome
MiniMed 640G with PLGS [58] 36 Mean sensor glucose and time
with hypoglycemia PLGS versus
LGS 160 21 mg/dL versus
153 21 mg/dL, P ¼ .002.
3.0 2.4 versus 4.1 3.2,
P ¼ .013
Medtronic MiniMed 640G pump 154 The average percentage of time
[48] spent in hypoglycemia (sensor
glucose < 63 mg/dL) PLGM
versus SAPT 1.5 versus 2.6,
P < .0001
MiniMed-640G with PLGS [59] 162 (real world) Hemoglobin A1 C and %
SMBG < 70 mg/dL{ 7.1 0.7
versus 7.2 0.8, P ¼ .33. 6 5
versus 10 7, P ¼ .001
Medtronic MiniMed 640G pump 68 Time and duration of PLGM-
[60] initiated pump suspension.
There were 20,183 suspend
before low events in 8523 days
(2.37 events/day). The mean
suspend duration was 55.0
e32.7 min (day 50.0 30.1,
night 71.7 35.1; P < .001).
Minimed 640G pump [61] 31 The time spent with BG levels
below 70 mg/dL with a threshold
of 90 versus 70 mg/dL 1.8
versus 2.3%
Statistical prediction algorithm 22 Number of hypoglycemic
[40] episodes that were prevented in
30 versus 45 min prediction
horizon (60% vs. 80%).
Five predictive alarm 26 Number of hypoglycemic
algorithms: episodes that were prevented.
Modified linear prediction alarm Hypoglycemia was prevented for
Kalman filtering 71% of the events (15 events).
Adaptive hybrid infinite impulse
response (HIIR) filter
Statistical prediction
Numerical logical algorithm [36]
Revel CGM device þ a 19 The primary safety outcomes
hypoglycemia prediction were fasting blood glucose
algorithm (Kalman filter-based Three algorithms (interventions
model) [43] vs. control)
158 versus 125
151 versus 138
144 versus 133
Efficacy outcome: Percentage of
nights with CGM 70 mg/dL
19% versus 26%
19% versus 33%
16% versus 30%