Page 449 - Handbook Of Integral Equations
P. 449
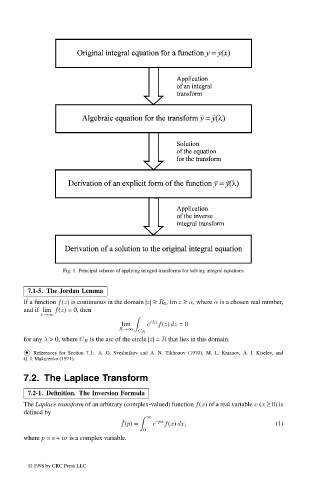
Fig. 1. Principal scheme of applying integral transforms for solving integral equations
7.1-5. The Jordan Lemma
If a function f(z) is continuous in the domain |z|≥ R 0 ,Im z ≥ α, where α is a chosen real number,
and if lim f(z) = 0, then
z→∞
lim e iλz f(z) dz =0
R→∞
C R
for any λ > 0, where C R is the arc of the circle |z| = R that lies in this domain.
•
References for Section 7.1: A. G. Sveshnikov and A. N. Tikhonov (1970), M. L. Krasnov, A. I. Kiselev, and
G. I. Makarenko (1971).
7.2. The Laplace Transform
7.2-1. Definition. The Inversion Formula
The Laplace transform of an arbitrary (complex-valued) function f(x) of a real variable x (x ≥ 0) is
defined by
∞
˜
f(p)= e –px f(x) dx, (1)
0
where p = s + iσ is a complex variable.
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
Page 430