Page 338 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 338
Computer modeling of interaction between a hydrate surface and an inhibitor 337
(3) Coverage of the surface. It was found that most polymers adsorb on periphery of
large hydrate cavities where water hydrogens pointing from surface are available
for hydrogen bonding. The largest amount of supercooling showed by PVCap was
35 °F for a 1600 MW polymer (Annual Report, 1996). This corresponds to a short
11-segment polymer. Shorter polymers adsorb flat on the surface and cover larger
area. However, a polymer shouldn't be too short because then it could desorb from
hydrate.
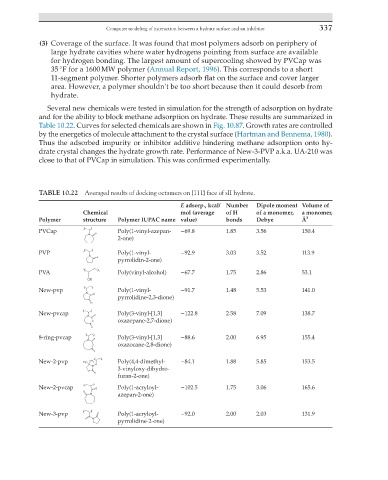
Several new chemicals were tested in simulation for the strength of adsorption on hydrate
and for the ability to block methane adsorption on hydrate. These results are summarized in
Table 10.22. Curves for selected chemicals are shown in Fig. 10.87. Growth rates are controlled
by the energetics of molecule attachment to the crystal surface (Hartman and Bennema, 1980).
Thus the adsorbed impurity or inhibitor additive hindering methane adsorption onto hy-
drate crystal changes the hydrate growth rate. Performance of New-3-PVP a.k.a. UA-210 was
close to that of PVCap in simulation. This was confirmed experimentally.
TABLE 10.22 Averaged results of docking octamers on {111} face of sII hydrate.
E adsorp., kcal/ Number Dipole moment Volume of
Chemical mol (average of H of a monomer, a monomer,
Polymer structure Polymer IUPAC name value) bonds Debye Å 3
PVCap Poly(1-vinyl-azepan- −69.8 1.85 3.56 150.4
2-one)
PVP Poly(1-vinyl- −92.9 3.03 3.52 113.9
pyrrolidin-2-one)
PVA Poly(vinyl-alcohol) −67.7 1.75 2.86 53.1
New-pvp Poly(1-vinyl- −91.7 1.48 5.53 141.0
pyrrolidine-2,3-dione)
New-pvcap Poly(3-vinyl-[1,3] −122.8 2.58 7.09 138.7
oxazepane-2,7-dione)
8-ring-pvcap Poly(3-vinyl-[1,3] −88.6 2.00 6.95 155.4
oxazocane-2,8-dione)
New-2-pvp Poly(4,4-dimethyl- −84.1 1.88 5.85 153.5
3-vinyloxy-dihydro-
furan-2-one)
New-2-pvcap Poly(1-acryloyl- −102.5 1.75 3.06 165.6
azepan-2-one)
New-3-pvp Poly(1-acryloyl- −92.0 2.00 2.03 131.9
pyrrolidine-2-one)