Page 68 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 68
Non-Newtonian behavior 63
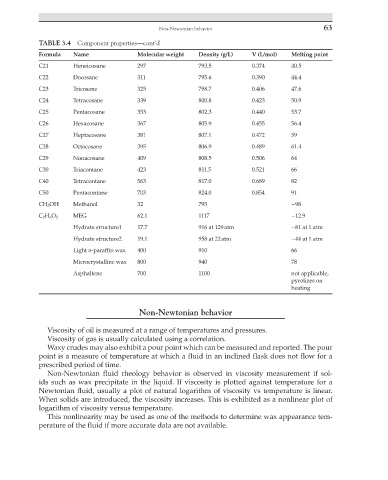
TABLE 3.4 Component properties—cont’d
Formula Name Molecular weight Density (g/L) V (L/mol) Melting point
C21 Heneicosane 297 793.5 0.374 40.5
C22 Docosane 311 795.6 0.390 44.4
C23 Tricosane 325 798.7 0.406 47.6
C24 Tetracosane 339 800.8 0.423 50.9
C25 Pentacosane 353 802.3 0.440 53.7
C26 Hexacosane 367 805.9 0.455 56.4
C27 Heptacosane 381 807.1 0.472 59
C28 Octacosane 395 806.9 0.489 61.4
C29 Nonacosane 409 808.5 0.506 64
C30 Triacontane 423 811.5 0.521 66
C40 Tetracontane 563 817.0 0.689 82
C50 Pentacontane 703 824.0 0.854 91
CH 3 OH Methanol 32 795 −98
C 2 H 6 O 2 MEG 62.1 1117 −12.9
Hydrate structure1 17.7 916 at 129 atm −81 at 1 atm
Hydrate structure2 19.1 958 at 22 atm −44 at 1 atm
Light n-paraffin wax 400 910 66
Microcrystalline wax 800 940 78
Asphaltene 700 1100 not applicable,
pyrolizes on
heating
Non-Newtonian behavior
Viscosity of oil is measured at a range of temperatures and pressures.
Viscosity of gas is usually calculated using a correlation.
Waxy crudes may also exhibit a pour point which can be measured and reported. The pour
point is a measure of temperature at which a fluid in an inclined flask does not flow for a
prescribed period of time.
Non-Newtonian fluid rheology behavior is observed in viscosity measurement if sol-
ids such as wax precipitate in the liquid. If viscosity is plotted against temperature for a
Newtonian fluid, usually a plot of natural logarithm of viscosity vs temperature is linear.
When solids are introduced, the viscosity increases. This is exhibited as a nonlinear plot of
logarithm of viscosity versus temperature.
This nonlinearity may be used as one of the methods to determine wax appearance tem-
perature of the fluid if more accurate data are not available.