Page 229 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 229
Section 3.0 - Non-Chloride Accelerators 211
Many inorganic and organic salts have been examined for their
action on the hydration of cement and cement compounds utilizing thermal
techniques. They include sodium and calcium salts of chloride, bromide,
nitrite, thiosulfate, thiocyanate, iodide, nitrate, hydroxide, carbonate, hy-
droxide, etc. A few typical examples are given illustrating the application
of thermal techniques in the investigation of these compounds on cements
and cement components.
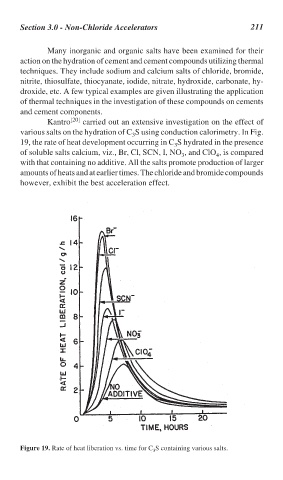
Kantro [20] carried out an extensive investigation on the effect of
various salts on the hydration of C S using conduction calorimetry. In Fig.
3
19, the rate of heat development occurring in C S hydrated in the presence
3
of soluble salts calcium, viz., Br, Cl, SCN, I, NO , and ClO , is compared
4
3
with that containing no additive. All the salts promote production of larger
amounts of heats and at earlier times. The chloride and bromide compounds
however, exhibit the best acceleration effect.
Figure 19. Rate of heat liberation vs. time for C S containing various salts.
3