Page 92 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 92
Section 2.0 - Raw Materials 75
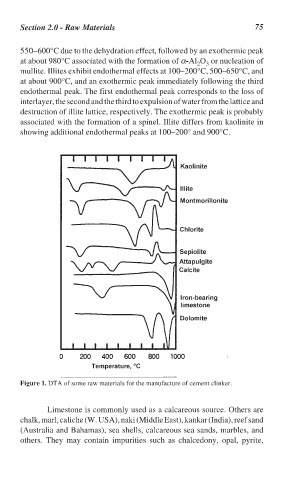
550–600°C due to the dehydration effect, followed by an exothermic peak
at about 980°C associated with the formation of α-Al O or nucleation of
3
2
mullite. Illites exhibit endothermal effects at 100–200°C, 500–650°C, and
at about 900°C, and an exothermic peak immediately following the third
endothermal peak. The first endothermal peak corresponds to the loss of
interlayer, the second and the third to expulsion of water from the lattice and
destruction of illite lattice, respectively. The exothermic peak is probably
associated with the formation of a spinel. Illite differs from kaolinite in
showing additional endothermal peaks at 100–200° and 900°C.
Figure 1. DTA of some raw materials for the manufacture of cement clinker.
Limestone is commonly used as a calcareous source. Others are
chalk, marl, caliche (W. USA), naki (Middle East), kankar (India), reef sand
(Australia and Bahamas), sea shells, calcareous sea sands, marbles, and
others. They may contain impurities such as chalcedony, opal, pyrite,