Page 15 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 15
8 Mechanisms of Adhesion
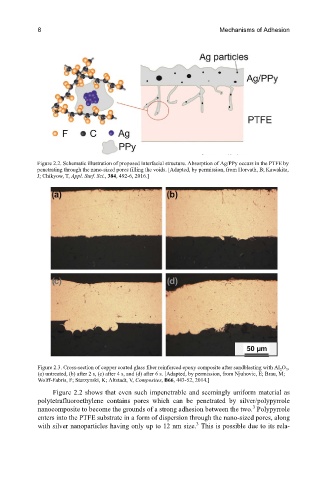
Figure 2.2. Schematic illustration of proposed interfacial structure. Absorption of Ag/PPy occurs in the PTFE by
penetrating through the nano-sized pores filling the voids. [Adapted, by permission, from Horvath, B; Kawakita,
J; Chikyow, T, Appl. Surf. Sci., 384, 492-6, 2016.]
Figure 2.3. Cross-section of copper coated glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite after sandblasting with Al O ,
3
2
(a) untreated, (b) after 2 s, (c) after 4 s, and (d) after 6 s. [Adapted, by permission, from Njuhovic, E; Brau, M;
Wolff-Fabris, F; Starzynski, K; Altstadt, V, Composites, B66, 443-52, 2014.]
Figure 2.2 shows that even such impenetrable and seemingly uniform material as
polytetrafluoroethylene contains pores which can be penetrated by silver/polypyrrole
3
nanocomposite to become the grounds of a strong adhesion between the two. Polypyrrole
enters into the PTFE substrate in a form of dispersion through the nano-sized pores, along
3
with silver nanoparticles having only up to 12 nm size. This is possible due to its rela-