Page 78 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 78
4.2 Surface treatment 71
-1
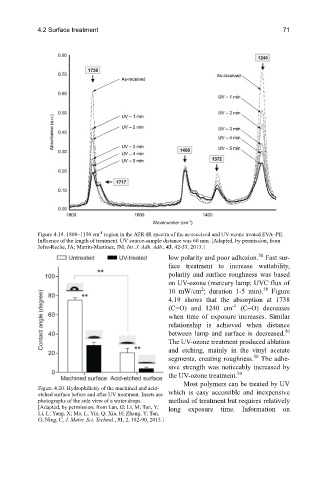
Figure 4.19. 1800–1150 cm region in the ATR-IR spectra of the as-received and UV-ozone treated EVA–PE.
Influence of the length of treatment. UV source-sample distance was 60 mm. [Adapted, by permission, from
Jofre-Reche, JA; Martín-Martínez, JM, Int. J. Adh. Adh., 43, 42-53, 2013.]
50
low polarity and poor adhesion. Fast sur-
face treatment to increase wettability,
polarity and surface roughness was based
on UV-ozone (mercury lamp; UVC flux of
2
50
10 mW/cm ; duration 1-5 min). Figure
4.19 shows that the absorption at 1738
-1
(C=O) and 1240 cm (C−O) decreases
when time of exposure increases. Similar
relationship is achieved when distance
between lamp and surface is decreased. 50
The UV-ozone treatment produced ablation
and etching, mainly in the vinyl acetate
50
segments, creating roughness. The adhe-
sive strength was noticeably increased by
50
the UV-ozone treatment.
Most polymers can be treated by UV
Figure 4.20. Hydrophilicity of the machined and acid- which is easy accessible and inexpensive
etched surface before and after UV treatment. Insets are
photographs of the side view of a water drops. method of treatment but requires relatively
[Adapted, by permission, from Lan, G; Li, M; Tan, Y; long exposure time. Information on
Li, L; Yang, X; Ma, L; Yin, Q; Xia, H; Zhang, Y; Tan,
G; Ning, C, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 31, 2, 182-90, 2015.]