Page 421 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 421
364 Chapter Ten
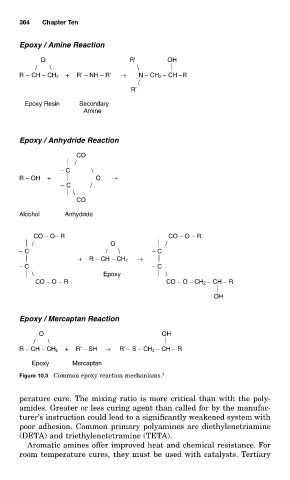
Epoxy / Amine Reaction
O R’ OH
/ \ \
R -- CH − CH 2 + R’ − NH − R’ → N − CH 2 − CH −R
/
R’
Epoxy Resin Secondary
Amine
Epoxy / Anhydride Reaction
CO
/
− C \
R − OH + O →
-- C /
\
CO
Alcohol Anhydride
CO − O − R CO − O − R
/ O /
− C / \ − C
+ R − CH − CH 2 →
− C − C
\ Epoxy \
CO − O − R CO − O − CH 2 − CH − R
OH
Epoxy / Mercaptan Reaction
O OH
/ \
R − CH − CH 2 + R’ − SH → R’ − S − CH 2 − CH − R
Epoxy Mercaptan
Figure 10.3 Common epoxy reaction mechanisms. 4
perature cure. The mixing ratio is more critical than with the poly-
amides. Greater or less curing agent than called for by the manufac-
turer’s instruction could lead to a significantly weakened system with
poor adhesion. Common primary polyamines are diethylenetriamine
(DETA) and triethylenetetramine (TETA).
Aromatic amines offer improved heat and chemical resistance. For
room temperature cures, they must be used with catalysts. Tertiary