Page 151 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 151
3.4 Reduced Manganese Oxides 119
3.4.2
Spinel-Type Compounds Mn 3 O 4 and γ -Mn 2 O 3
Both compounds Mn 3 O 4 (i.e., hausmannite) and γ -Mn 2 O 3 crystallize with a
tetragonally distorted spinel-type structure (see Figure 3.17).
2+
3+
Hausmannite has the composition (Mn )(Mn ) 2 O 3. In this tetragonal spinel
the bivalent cations are coordinated tetrahedrally, while the Mn 3+ ions have an
octahedral environment. The Mn 2+ ion can be replaced by other divalent ions
2+
with nearly the same radius (e.g., Zn ; in zinc-containing manganese dioxide
batteries heterolyte ZnMn 2 O 4 , which is isotypic with Mn 3 O 4 and may form a
solid solution with it, can be observed). If the synthesis of Mn 3 O 4 is performed
under oxidizing conditions, materials with XRD patterns very similar to that of
Mn 3 O 4 can be found, but the oxidation state is significantly higher than that
of hausmannite. Verwey and De Boer [106] proposed the name of γ -Mn 2 O 3 for
samples of the composition MnO 1.39 –MnO 1.5 . Goodenough and Loeb [107] found
that γ -Mn 2 O 3 crystallizes with the tetragonally distorted spinel-type structure of
Mn 3 O 4 but with significant defects (one-third) at the tetrahedrally coordinated
Mn 3+ site.
3.4.3
Pyrochroite, Mn(OH) 2
Pyrochroite, Mn(OH) 2 , is isotypic with brucite, Mg(OH) 2 . The crystal structure
consists of layers of edge-sharing Mn(OH) 6 octahedra. The layers are held together
by hydrogen bonding, as shown in Figure 3.18. Mn(OH) 2 represents the manganese
compounds with the lowest valence occurring in aqueous systems. Pyrochroite is
easily oxidized in the presence of oxygen, even at ambient condition, and therefore
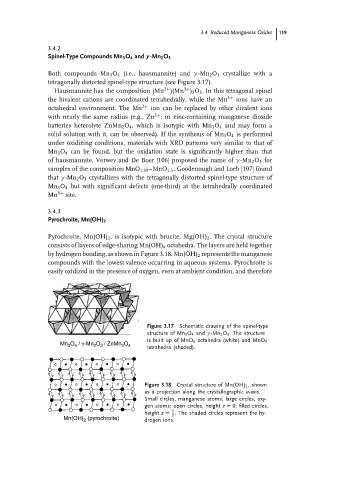
Figure 3.17 Schematic drawing of the spinel-type
structure of Mn 3 O 4 and γ -Mn 2 O 3 . The structure
is built up of MnO 6 octahedra (white) and MnO 4
Mn 3 O 4 / γ-Mn 2 O 3 / ZnMn 2 O 4
tetrahedra (shaded).
Figure 3.18 Crystal structure of Mn(OH) 2 , shown
as a projection along the crystallographic a-axis.
Small circles, manganese atoms; large circles, oxy-
gen atoms; open circles, height z = 0; filled circles,
1
height z = . The shaded circles represent the hy-
Mn(OH) 2 (pyrochroite) drogen ions. 2