Page 57 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 57
1.4 Criteria for the Judgment of Batteries 23
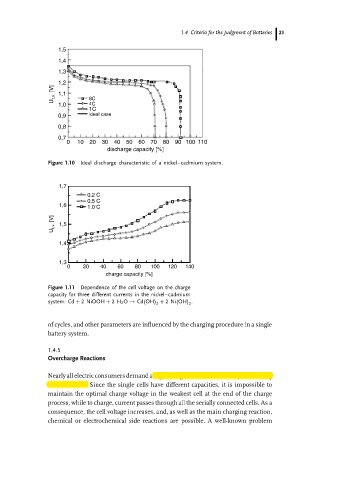
1,5
1,4
1,3
1,2
U t.v. [V] 1,1 8C
1,0 4C
1C
0,9 ideal case
0,8
0,7
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
discharge capacity [%]
Figure 1.10 Ideal discharge characteristic of a nickel–cadmium system.
1,7
0.2 C
0.5 C
1,6 1.0 C
U t.v. [V] 1,5
1,4
1,3
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
charge capacity [%]
Figure 1.11 Dependence of the cell voltage on the charge
capacity for three different currents in the nickel–cadmium
system: Cd + 2 NiOOH + 2H 2 O → Cd(OH) + 2 Ni(OH) .
2 2
of cycles, and other parameters are influenced by the charging procedure in a single
battery system.
1.4.5
Overcharge Reactions
Nearly all electric consumers demand a high voltage, which is realized by connecting
cells in series. Since the single cells have different capacities, it is impossible to
maintain the optimal charge voltage in the weakest cell at the end of the charge
process, while to charge, current passes through all the serially connected cells. As a
consequence, the cell voltage increases, and, as well as the main charging reaction,
chemical or electrochemical side reactions are possible. A well-known problem