Page 79 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 79
2.5 Lithium Primary Batteries 45
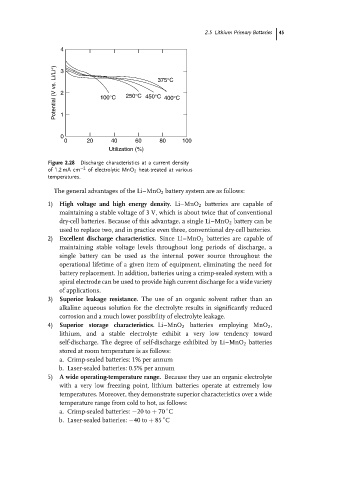
4 3
Potential (V vs. Li/Li + ) 2 1 100°C 250°C 450°C 375°C
400°C
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
Utilization (%)
Figure 2.28 Discharge characteristics at a current density
of 1.2 mA cm −2 of electrolytic MnO 2 heat-treated at various
temperatures.
The general advantages of the Li–MnO 2 battery system are as follows:
1) High voltage and high energy density. Li–MnO 2 batteries are capable of
maintaining a stable voltage of 3 V, which is about twice that of conventional
dry-cell batteries. Because of this advantage, a single Li–MnO 2 battery can be
used to replace two, and in practice even three, conventional dry-cell batteries.
2) Excellent discharge characteristics. Since Li–MnO 2 batteries are capable of
maintaining stable voltage levels throughout long periods of discharge, a
single battery can be used as the internal power source throughout the
operational lifetime of a given item of equipment, eliminating the need for
battery replacement. In addition, batteries using a crimp-sealed system with a
spiral electrode can be used to provide high current discharge for a wide variety
of applications.
3) Superior leakage resistance. The use of an organic solvent rather than an
alkaline aqueous solution for the electrolyte results in significantly reduced
corrosion and a much lower possibility of electrolyte leakage.
4) Superior storage characteristics. Li–MnO 2 batteries employing MnO 2 ,
lithium, and a stable electrolyte exhibit a very low tendency toward
self-discharge. The degree of self-discharge exhibited by Li–MnO 2 batteries
stored at room temperature is as follows:
a. Crimp-sealed batteries: 1% per annum
b. Laser-sealed batteries: 0.5% per annum
5) A wide operating-temperature range. Because they use an organic electrolyte
with a very low freezing point, lithium batteries operate at extremely low
temperatures. Moreover, they demonstrate superior characteristics over a wide
temperature range from cold to hot, as follows:
◦
a. Crimp-sealed batteries: −20 to + 70 C
◦
b. Laser-sealed batteries: −40 to + 85 C