Page 76 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 76
42 2 Practical Batteries
2.0
1.0
1 as-cast
0.5 2 annealed
3 rapidly quenched
Pressure (MPa) 0.2
4 rapidly quenched and annealed
0.1
1
0.05
4
0.02
3
2
0.01
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
H/M
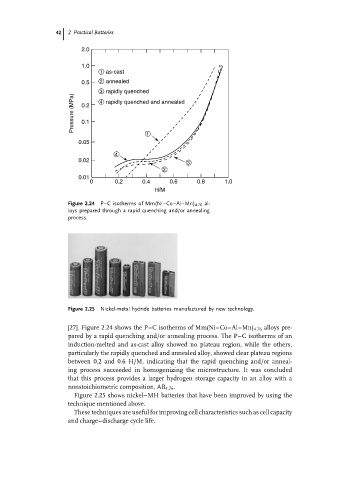
Figure 2.24 P–C isotherms of Mm(Ni–Co–Al–Mn) 4.76 al-
loys prepared through a rapid quenching and/or annealing
process.
Figure 2.25 Nickel-metal hydride batteries manufactured by new technology.
[27]. Figure 2.24 shows the P–C isotherms of Mm(Ni–Co–Al–Mn) 4.76 alloys pre-
pared by a rapid quenching and/or annealing process. The P–C isotherms of an
induction-melted and as-cast alloy showed no plateau region, while the others,
particularly the rapidly quenched and annealed alloy, showed clear plateau regions
between 0.2 and 0.6 H/M, indicating that the rapid quenching and/or anneal-
ing process succeeded in homogenizing the microstructure. It was concluded
that this process provides a larger hydrogen storage capacity in an alloy with a
nonstoichiometric composition, AB 4.76 .
Figure 2.25 shows nickel–MH batteries that have been improved by using the
technique mentioned above.
These techniques are useful for improving cell characteristics such as cell capacity
and charge–discharge cycle life.