Page 73 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 73
2.4 Nickel–MH Batteries 39
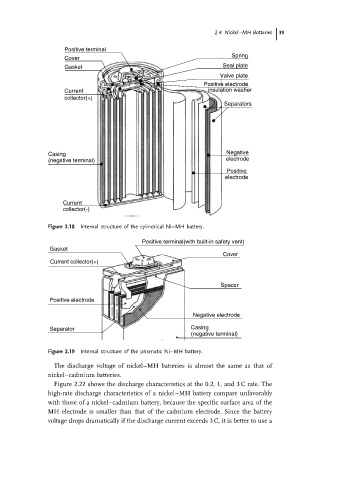
Positive terminal
Spring
Cover
Gasket Seal plate
Valve plate
Positive electrode
Current insulation washer
collector(+)
Separators
Casing Negative
(negative terminal) electrode
Positive
electrode
Current
collector(-)
Figure 2.18 Internal structure of the cylindrical Ni–MH battery.
Positive terminal(with built-in safety vent)
Gasket
Cover
Current collector(+)
Spacer
Positive electrode
Negative electrode
Separator Casing
(negative terminal)
Figure 2.19 Internal structure of the prismatic Ni–MH battery.
The discharge voltage of nickel–MH batteries is almost the same as that of
nickel–cadmium batteries.
Figure 2.22 shows the discharge characteristics at the 0.2, 1, and 3 C rate. The
high-rate discharge characteristics of a nickel–MH battery compare unfavorably
with those of a nickel–cadmium battery, because the specific surface area of the
MH electrode is smaller than that of the cadmium electrode. Since the battery
voltage drops dramatically if the discharge current exceeds 3 C, it is better to use a