Page 222 - Handbook of Biomechatronics
P. 222
Upper-Limb Prosthetic Devices 219
2.6 BIONs and IMESs
2.6.1 Alfred E. Mann Foundation
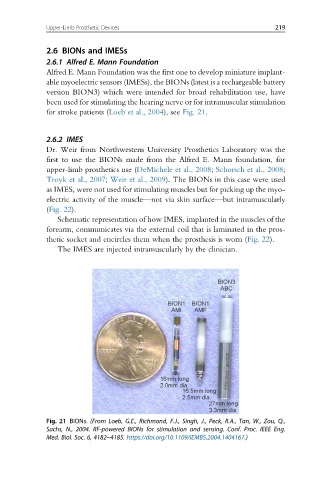
Alfred E. Mann Foundation was the first one to develop miniature implant-
able myoelectric sensors (IMESs), the BIONs (latest is a rechargeable battery
version BION3) which were intended for broad rehabilitation use, have
been used for stimulating the hearing nerve or for intramuscular stimulation
for stroke patients (Loeb et al., 2004), see Fig. 21.
2.6.2 IMES
Dr. Weir from Northwestern University Prosthetics Laboratory was the
first to use the BIONs made from the Alfred E. Mann foundation, for
upper-limb prosthetics use (DeMichele et al., 2008; Schorsch et al., 2008;
Troyk et al., 2007; Weir et al., 2009). The BIONs in this case were used
as IMES, were not used for stimulating muscles but for picking up the myo-
electric activity of the muscle—not via skin surface—but intramuscularly
(Fig. 22).
Schematic representation of how IMES, implanted in the muscles of the
forearm, communicates via the external coil that is laminated in the pros-
thetic socket and encircles them when the prosthesis is worn (Fig. 22).
The IMES are injected intramuscularly by the clinician.
Fig. 21 BIONs. (From Loeb, G.E., Richmond, F.J., Singh, J., Peck, R.A., Tan, W., Zou, Q.,
Sachs, N., 2004. RF-powered BIONs for stimulation and sensing. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng.
Med. Biol. Soc. 6, 4182–4185. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2004.1404167.)