Page 454 - Handbook of Biomechatronics
P. 454
448 Graham Brooker
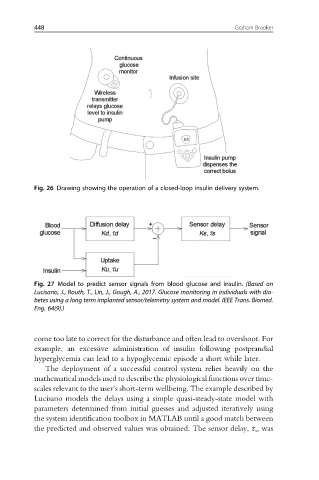
Fig. 26 Drawing showing the operation of a closed-loop insulin delivery system.
Fig. 27 Model to predict sensor signals from blood glucose and insulin. (Based on
Lucisano, J., Routh, T., Lin, J., Gough, A., 2017. Glucose monitoring in individuals with dia-
betes using a long term implanted sensor/telemetry system and model. IEEE Trans. Biomed.
Eng. 64(9).)
come too late to correct for the disturbance and often lead to overshoot. For
example, an excessive administration of insulin following postprandial
hyperglycemia can lead to a hypoglycemic episode a short while later.
The deployment of a successful control system relies heavily on the
mathematical models used to describe the physiological functions over time-
scales relevant to the user’s short-term wellbeing. The example described by
Lucisano models the delays using a simple quasi-steady-state model with
parameters determined from initial guesses and adjusted iteratively using
the system identification toolbox in MATLAB until a good match between
the predicted and observed values was obtained. The sensor delay, τ s , was