Page 127 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 127
INDUCTION MOTORS 109
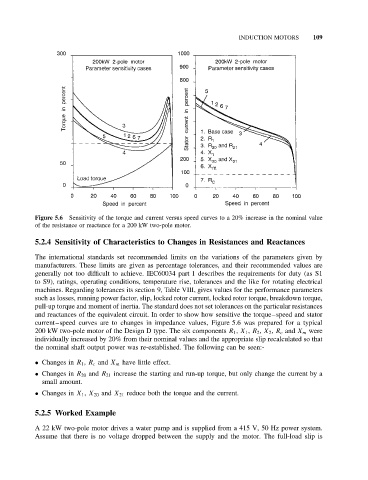
Figure 5.6 Sensitivity of the torque and current versus speed curves to a 20% increase in the nominal value
of the resistance or reactance for a 200 kW two-pole motor.
5.2.4 Sensitivity of Characteristics to Changes in Resistances and Reactances
The international standards set recommended limits on the variations of the parameters given by
manufacturers. These limits are given as percentage tolerances, and their recommended values are
generally not too difficult to achieve. IEC60034 part 1 describes the requirements for duty (as S1
to S9), ratings, operating conditions, temperature rise, tolerances and the like for rotating electrical
machines. Regarding tolerances its section 9, Table VIII, gives values for the performance parameters
such as losses, running power factor, slip, locked rotor current, locked rotor torque, breakdown torque,
pull-up torque and moment of inertia. The standard does not set tolerances on the particular resistances
and reactances of the equivalent circuit. In order to show how sensitive the torque–speed and stator
current–speed curves are to changes in impedance values, Figure 5.6 was prepared for a typical
200 kW two-pole motor of the Design D type. The six components R 1 , X 1 , R 2 , X 2 , R c and X m were
individually increased by 20% from their nominal values and the appropriate slip recalculated so that
the nominal shaft output power was re-established. The following can be seen:-
• Changes in R 1 , R c and X m have little effect.
• Changes in R 20 and R 21 increase the starting and run-up torque, but only change the current by a
small amount.
• Changes in X 1 , X 20 and X 21 reduce both the torque and the current.
5.2.5 Worked Example
A 22 kW two-pole motor drives a water pump and is supplied from a 415 V, 50 Hz power system.
Assume that there is no voltage dropped between the supply and the motor. The full-load slip is