Page 206 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 206
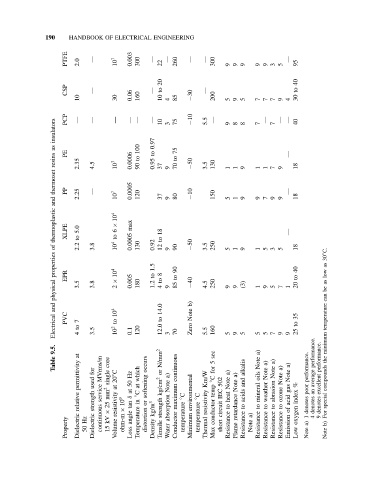
190 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
PTFE 2.0 — 10 7 0.003 300 — 22 — 260 — — 300 9 9 9 9 9 3 5 — 95
CSP — — 10to20 — 40 to
10 30 0.06 160 4 85 −30 200 5 9 5 7 7 7 9 4 30
insulators PCP — — — — — — 10 3 75 −10 5.5 — 9 8 8 7 — 7 — — 40
as 100 0.97 75
resins PE 2.35 4.5 10 7 0.0006 to 90 to 0.95 37 9 to 70 −50 3.5 130 1 1 9 1 1 7 9 — 18
thermoset PP — 0.0005 —
and 2.25 10 7 120 37 9 80 −10 150 5 1 9 9 7 9 9 18
thermoplastic XLPE 5.0 10 4 6 × max 18 —
of to 2.2 3.8 to 10 4 0.0005 130 0.92 12to 9 90 −50 3.5 250 5 1 9 1 5 3 5 18 30 ◦ C.
properties EPR 10 4 1.5 to 90 to 40 to as low
physical 3.5 3.8 × 2 0.005 180 1.2 4to8 9 85 −40 4.5 250 9 9 (3) 1 9 5 7 1 20 as be can
and 10 4 14.0 b) Note 35 temperature
Electrical PVC 7 to 4 3.5 to 10 2 0.1 120 12.0to 3 70 Zero 5.5 160 5 9 5 5 5 7 9 9 to 25
9.5. at a) performance. minimum
Table MVrms/m core occurs N/mm 2 continuous 5sec alkalis Note a) a) a) a) performance. performance. the
permittivity for used single 20 ◦ C at Hz 50 ◦ Catwhich softening or kg/cm 2 a) Note Km/W ◦ Cfor 502 a) Note a) Note and oils Note Note Note Note gas % average excellent compounds
relative strength service mm 2 25 × resistivity 10 9 × at δ tan in or kg/m 3 strength absorption maximum ◦ C environmental ◦ C resistivity temp conductor IEC circuit heat to retardance acids to mineral to weather to abrasion to ozone to acid of index poor denotes an denotes denotes special For
Property Dielectric Hz 50 Dielectric continuous kV 15 Volume ohm-m angle Loss Temperature distortion Density Tensile Water Conductor temperature Minimum temperature Thermal Max short Resistance Flame Resistance a) Note Resistance Resistance Resistance Resistance Emission oxygen Low 1 a) Note 4 9 b) Note