Page 290 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 290
276 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
11.5.2 Calculation of Fault Current – rms Symmetrical Values
From sub-section 11.5.1 the emf E (E , E or E) and appropriate reactance X (X , X or X sd ) are
d d
known. Hence the symmetrical fault current I f may be easily calculated:
E
I f = per unit
X
For example:
A 6600 V, 4.13 MVA generator has X = 15.5%, X = 23.5% and X sd = 205%
d d
At full load with a power factor of 0.8 lagging the corresponding emfs are therefore:
E = 1.1pu,E = 1.156 pu and E = 2.77 pu
The rms fault currents are therefore:
1.1
I = = 7.097 pu (2564 amps)
f
0.155
1.156
I = = 4.919 pu (1776 amps)
f
0235
2.77
I f = = 1.351 pu (488 amps)
2.05
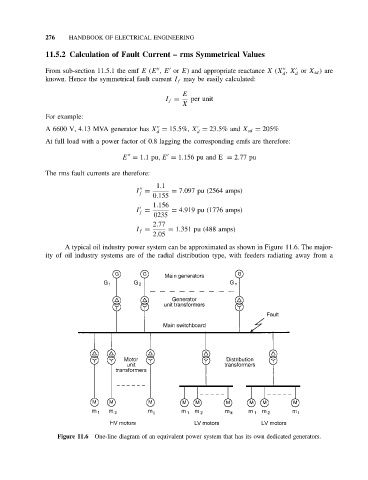
A typical oil industry power system can be approximated as shown in Figure 11.6. The major-
ity of oil industry systems are of the radial distribution type, with feeders radiating away from a
Figure 11.6 One-line diagram of an equivalent power system that has its own dedicated generators.