Page 266 - Handbook of Instrumental Techniques for Analytical Chemistry
P. 266
256 Handbook of Instrumental Techniques for Analytical Chemistry
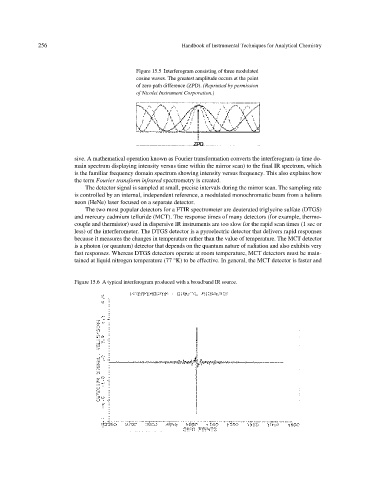
Figure 15.5 Interferogram consisting of three modulated
cosine waves. The greatest amplitude occurs at the point
of zero path difference (ZPD). (Reprinted by permission
of Nicolet Instrument Corporation.)
sive. A mathematical operation known as Fourier transformation converts the interferogram (a time do-
main spectrum displaying intensity versus time within the mirror scan) to the final IR spectrum, which
is the familiar frequency domain spectrum showing intensity versus frequency. This also explains how
the term Fourier transform infrared spectrometry is created.
The detector signal is sampled at small, precise intervals during the mirror scan. The sampling rate
is controlled by an internal, independent reference, a modulated monochromatic beam from a helium
neon (HeNe) laser focused on a separate detector.
The two most popular detectors for a FTIR spectrometer are deuterated triglycine sulfate (DTGS)
and mercury cadmium telluride (MCT). The response times of many detectors (for example, thermo-
couple and thermistor) used in dispersive IR instruments are too slow for the rapid scan times (1 sec or
less) of the interferometer. The DTGS detector is a pyroelectric detector that delivers rapid responses
because it measures the changes in temperature rather than the value of temperature. The MCT detector
is a photon (or quantum) detector that depends on the quantum nature of radiation and also exhibits very
fast responses. Whereas DTGS detectors operate at room temperature, MCT detectors must be main-
tained at liquid nitrogen temperature (77 °K) to be effective. In general, the MCT detector is faster and
Figure 15.6 A typical interferogram produced with a broadband IR source.