Page 192 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 192
188 CHAPTER 8 Seismic risk of RC water storage elevated tanks
1 INTRODUCTION
The phenomenon of earthquakes is not new or specific to Algeria. It appears cycli-
cally from one region to another causing sometimes immeasurable damage that no
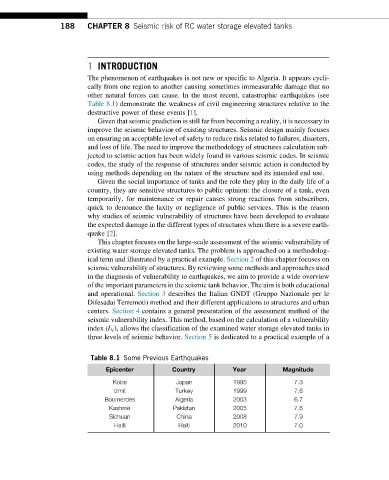
other natural forces can cause. In the most recent, catastrophic earthquakes (see
Table 8.1) demonstrate the weakness of civil engineering structures relative to the
destructive power of these events [1].
Given that seismic prediction is still far from becoming a reality, it is necessary to
improve the seismic behavior of existing structures. Seismic design mainly focuses
on ensuring an acceptable level of safety to reduce risks related to failures, disasters,
and loss of life. The need to improve the methodology of structures calculation sub-
jected to seismic action has been widely found in various seismic codes. In seismic
codes, the study of the response of structures under seismic action is conducted by
using methods depending on the nature of the structure and its intended end use.
Given the social importance of tanks and the role they play in the daily life of a
country, they are sensitive structures to public opinion: the closure of a tank, even
temporarily, for maintenance or repair causes strong reactions from subscribers,
quick to denounce the laxity or negligence of public services. This is the reason
why studies of seismic vulnerability of structures have been developed to evaluate
the expected damage in the different types of structures when there is a severe earth-
quake [2].
This chapter focuses on the large-scale assessment of the seismic vulnerability of
existing water storage elevated tanks. The problem is approached on a methodolog-
ical term and illustrated by a practical example. Section 2 of this chapter focuses on
seismic vulnerability of structures. By reviewing some methods and approaches used
in the diagnosis of vulnerability to earthquakes, we aim to provide a wide overview
of the important parameters in the seismic tank behavior. The aim is both educational
and operational. Section 3 describes the Italian GNDT (Gruppo Nazionale per le
Difesadai Terremoti) method and their different applications to structures and urban
centers. Section 4 contains a general presentation of the assessment method of the
seismic vulnerability index. This method, based on the calculation of a vulnerability
index (I V ), allows the classification of the examined water storage elevated tanks in
three levels of seismic behavior. Section 5 is dedicated to a practical example of a
Table 8.1 Some Previous Earthquakes
Epicenter Country Year Magnitude
Kobe Japan 1995 7.3
Izmit Turkey 1999 7.6
Boumerdes Algeria 2003 6.7
Kashmir Pakistan 2005 7.6
Sichuan China 2008 7.9
Haiti Haiti 2010 7.0