Page 224 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 224
220 CHAPTER 9 Reliability and failure analysis of wastewater systems
% Length of pipes
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
2.5%
Steel 8.3%
12.7%
26.5%
Gray cast iron 48.8%
36.9%
26%
Nodular cast iron 35.5%
3.3%
27.8%
PVC 1.1%
27.3%
4%
PE 5.9%
15.1%
0.2%
Concrete
13.1%
Lead
Asbestos cement 0.4%
0.4%
other: GRP, reinforced concrete
0.3%
France Austria Poland
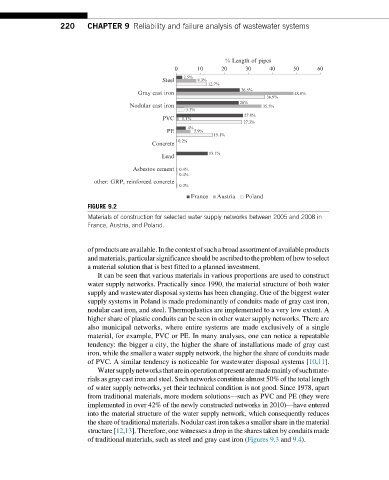
FIGURE 9.2
Materials of construction for selected water supply networks between 2005 and 2008 in
France, Austria, and Poland.
ofproductsare available.In thecontext ofsucha broadassortmentofavailable products
and materials, particular significance should be ascribed to the problem of how to select
a material solution that is best fitted to a planned investment.
It can be seen that various materials in various proportions are used to construct
water supply networks. Practically since 1990, the material structure of both water
supply and wastewater disposal systems has been changing. One of the biggest water
supply systems in Poland is made predominantly of conduits made of gray cast iron,
nodular cast iron, and steel. Thermoplastics are implemented to a very low extent. A
higher share of plastic conduits can be seen in other water supply networks. There are
also municipal networks, where entire systems are made exclusively of a single
material, for example, PVC or PE. In many analyses, one can notice a repeatable
tendency: the bigger a city, the higher the share of installations made of gray cast
iron, while the smaller a water supply network, the higher the share of conduits made
of PVC. A similar tendency is noticeable for wastewater disposal systems [10,11].
Watersupplynetworksthatareinoperationatpresentaremademainlyofsuchmate-
rials as gray cast iron and steel. Such networks constitute almost 50% of the total length
of water supply networks, yet their technical condition is not good. Since 1978, apart
from traditional materials, more modern solutions—such as PVC and PE (they were
implemented in over 42% of the newly constructed networks in 2010)—have entered
into the material structure of the water supply network, which consequently reduces
the share of traditional materials. Nodular cast iron takes a smaller share in the material
structure [12,13]. Therefore, one witnesses a drop in the shares taken by conduits made
of traditional materials, such as steel and gray cast iron (Figures 9.3 and 9.4).