Page 228 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 228
224 CHAPTER 9 Reliability and failure analysis of wastewater systems
35
30
Number of damages (%) 20 PE
25
PVC
15
Steel
Cast iron
10
5 Asbestos cement
0
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012
Year
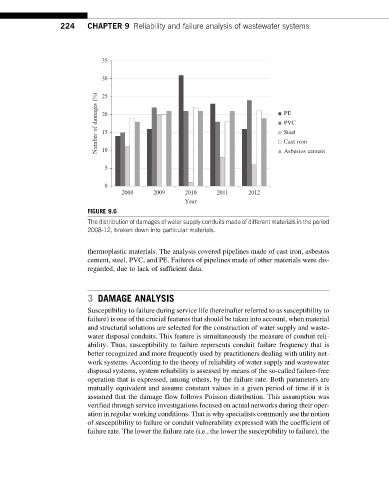
FIGURE 9.6
The distribution of damages of water supply conduits made of different materials in the period
2008-12, broken down into particular materials.
thermoplastic materials. The analysis covered pipelines made of cast iron, asbestos
cement, steel, PVC, and PE. Failures of pipelines made of other materials were dis-
regarded, due to lack of sufficient data.
3 DAMAGE ANALYSIS
Susceptibility to failure during service life (hereinafter referred to as susceptibility to
failure) is one of the crucial features that should be taken into account, when material
and structural solutions are selected for the construction of water supply and waste-
water disposal conduits. This feature is simultaneously the measure of conduit reli-
ability. Thus, susceptibility to failure represents conduit failure frequency that is
better recognized and more frequently used by practitioners dealing with utility net-
work systems. According to the theory of reliability of water supply and wastewater
disposal systems, system reliability is assessed by means of the so-called failure-free
operation that is expressed, among others, by the failure rate. Both parameters are
mutually equivalent and assume constant values in a given period of time if it is
assumed that the damage flow follows Poisson distribution. This assumption was
verified through service investigations focused on actual networks during their oper-
ation in regular working conditions. That is why specialists commonly use the notion
of susceptibility to failure or conduit vulnerability expressed with the coefficient of
failure rate. The lower the failure rate (i.e., the lower the susceptibility to failure), the