Page 234 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 234
230 CHAPTER 9 Reliability and failure analysis of wastewater systems
The highest susceptibility to failure was identified in the case of steel conduits
that are usually the oldest ones, while the lowest failure rate was identified in the
case of conduits made of thermoplastics. The research carried out in Poland [10]
yielded average values of failure rate within the range of 0-0.69 failures/km.
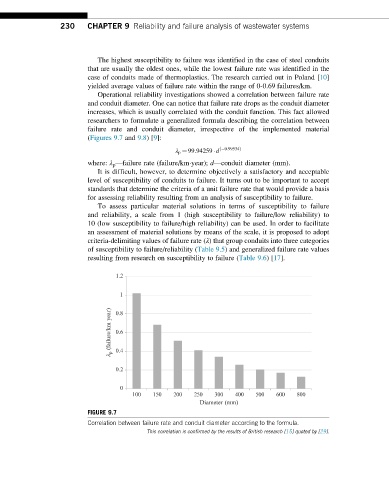
Operational reliability investigations showed a correlation between failure rate
and conduit diameter. One can notice that failure rate drops as the conduit diameter
increases, which is usually correlated with the conduit function. This fact allowed
researchers to formulate a generalized formula describing the correlation between
failure rate and conduit diameter, irrespective of the implemented material
(Figures 9.7 and 9.8)[9]:
λ p ¼ 99:94259 d ð 0:99534Þ
where: λ p —failure rate (failure/km year); d—conduit diameter (mm).
It is difficult, however, to determine objectively a satisfactory and acceptable
level of susceptibility of conduits to failure. It turns out to be important to accept
standards that determine the criteria of a unit failure rate that would provide a basis
for assessing reliability resulting from an analysis of susceptibility to failure.
To assess particular material solutions in terms of susceptibility to failure
and reliability, a scale from 1 (high susceptibility to failure/low reliability) to
10 (low susceptibility to failure/high reliability) can be used. In order to facilitate
an assessment of material solutions by means of the scale, it is proposed to adopt
criteria-delimiting values of failure rate (λ) that group conduits into three categories
of susceptibility to failure/reliability (Table 9.5) and generalized failure rate values
resulting from research on susceptibility to failure (Table 9.6)[17].
1.2
1
l p (failure/km year) 0.6
0.8
0.4
0.2
0
100 150 200 250 300 400 500 600 800
Diameter (mm)
FIGURE 9.7
Correlation between failure rate and conduit diameter according to the formula.
This correlation is confirmed by the results of British research [15] quoted by [29].