Page 235 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 235
4 Reliability of Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal Infrastructure 231
0.30
0.25
Failure (failure/km year) 0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0.00
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
Diameter (mm)
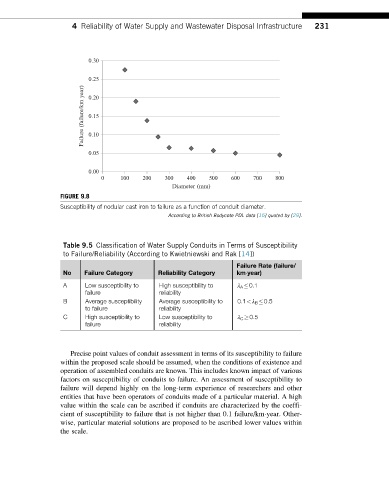
FIGURE 9.8
Susceptibility of nodular cast iron to failure as a function of conduit diameter.
According to British Bodycote PDL data [15] quoted by [29].
Table 9.5 Classification of Water Supply Conduits in Terms of Susceptibility
to Failure/Reliability (According to Kwietniewski and Rak [14])
Failure Rate (failure/
No Failure Category Reliability Category km year)
A Low susceptibility to High susceptibility to λ A 0.1
failure reliability
B Average susceptibility Average susceptibility to 0.1<λ B 0.5
to failure reliability
C High susceptibility to Low susceptibility to λ C 0.5
failure reliability
Precise point values of conduit assessment in terms of its susceptibility to failure
within the proposed scale should be assumed, when the conditions of existence and
operation of assembled conduits are known. This includes known impact of various
factors on susceptibility of conduits to failure. An assessment of susceptibility to
failure will depend highly on the long-term experience of researchers and other
entities that have been operators of conduits made of a particular material. A high
value within the scale can be ascribed if conduits are characterized by the coeffi-
cient of susceptibility to failure that is not higher than 0.1 failure/km year. Other-
wise, particular material solutions are proposed to be ascribed lower values within
the scale.