Page 238 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 238
234 CHAPTER 9 Reliability and failure analysis of wastewater systems
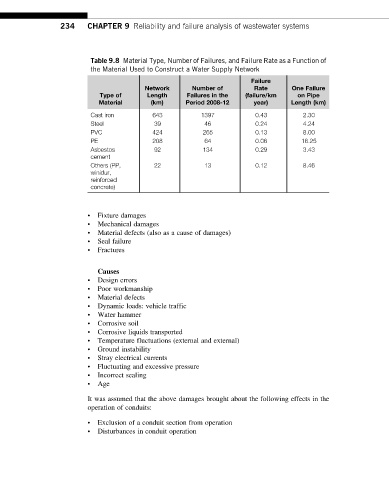
Table 9.8 Material Type, Number of Failures, and Failure Rate as a Function of
the Material Used to Construct a Water Supply Network
Failure
Network Number of Rate One Failure
Type of Length Failures in the (failure/km on Pipe
Material (km) Period 2008-12 year) Length (km)
Cast iron 643 1397 0.43 2.30
Steel 39 46 0.24 4.24
PVC 424 265 0.13 8.00
PE 208 64 0.06 16.25
Asbestos 92 134 0.29 3.43
cement
Others (PP, 22 13 0.12 8.46
winidur,
reinforced
concrete)
• Fixture damages
• Mechanical damages
• Material defects (also as a cause of damages)
• Seal failure
• Fractures
Causes
• Design errors
• Poor workmanship
• Material defects
• Dynamic loads: vehicle traffic
• Water hammer
• Corrosive soil
• Corrosive liquids transported
• Temperature fluctuations (external and external)
• Ground instability
• Stray electrical currents
• Fluctuating and excessive pressure
• Incorrect sealing
• Age
It was assumed that the above damages brought about the following effects in the
operation of conduits:
• Exclusion of a conduit section from operation
• Disturbances in conduit operation