Page 101 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 101
THERMOPLASTICS
THERMOPLASTICS 2.41
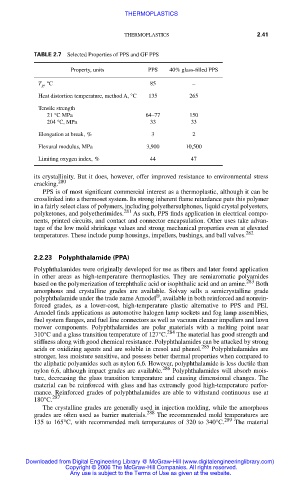
TABLE 2.7 Selected Properties of PPS and GF PPS
Property, units PPS 40% glass-filled PPS
T , °C 85 –
g
Heat distortion temperature, method A, °C 135 265
Tensile strength
21 °C MPa 64–77 150
204 °C, MPa 33 33
Elongation at break, % 3 2
Flexural modulus, MPa 3,900 10,500
Limiting oxygen index, % 44 47
its crystallinity. But it does, however, offer improved resistance to environmental stress
280
cracking.
PPS is of most significant commercial interest as a thermoplastic, although it can be
crosslinked into a thermoset system. Its strong inherent flame retardance puts this polymer
in a fairly select class of polymers, including polyethersulphones, liquid crystal polyesters,
281
polyketones, and polyetherimides. As such, PPS finds application in electrical compo-
nents, printed circuits, and contact and connector encapsulation. Other uses take advan-
tage of the low mold shrinkage values and strong mechanical properties even at elevated
282
temperatures. These include pump housings, impellers, bushings, and ball valves.
2.2.23 Polyphthalamide (PPA)
Polyphthalamides were originally developed for use as fibers and later found application
in other areas as high-temperature thermoplastics. They are semiaromatic polyamides
283
based on the polymerization of terephthalic acid or isophthalic acid and an amine. Both
amorphous and crystalline grades are available. Solvay sells a semicrystalline grade
®
polyphthalamide under the trade name Amodel , available in both reinforced and nonrein-
forced grades, as a lower-cost, high-temperature plastic alternative to PPS and PEI.
Amodel finds applications as automotive halogen lamp sockets and fog lamp assemblies,
fuel system flanges, and fuel line connectors as well as vacuum cleaner impellers and lawn
mower components. Polyphthalamides are polar materials with a melting point near
284
310°C and a glass transition temperature of 127°C. The material has good strength and
stiffness along with good chemical resistance. Polyphthalamides can be attacked by strong
285
acids or oxidizing agents and are soluble in cresol and phenol. Polyphthalamides are
stronger, less moisture sensitive, and possess better thermal properties when compared to
the aliphatic polyamides such as nylon 6,6. However, polyphthalamide is less ductile than
286
nylon 6,6, although impact grades are available. Polyphthalamides will absorb mois-
ture, decreasing the glass transition temperature and causing dimensional changes. The
material can be reinforced with glass and has extremely good high-temperature perfor-
mance. Reinforced grades of polyphthalamides are able to withstand continuous use at
287
180°C.
The crystalline grades are generally used in injection molding, while the amorphous
288
grades are often used as barrier materials. The recommended mold temperatures are
289
135 to 165°C, with recommended melt temperatures of 320 to 340°C. The material
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.