Page 29 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 29
INTRODUCTION TO POLYMERS AND PLASTICS
INTRODUCTION TO POLYMERS AND PLASTICS 1.15
TABLE 1.5 Typical Viscosities
Material Viscosity (Pa-s)
Air 10 –5
Water 10 –3
Polymer latexes 10 –2
Olive oil 10 –1
Glycerin 1
2
Polymer melts 10 – 10 6
Pitch 10 9
Plastics 10 12
Glass 10 21
TABLE 1.6 Typical Shear Rates for Selected
Processes 52
Process Shear rate (s-1)
Compression molding 1–10
Calendering 10–100
Extrusion 100–1,000
Injection molding 1,000–10,000
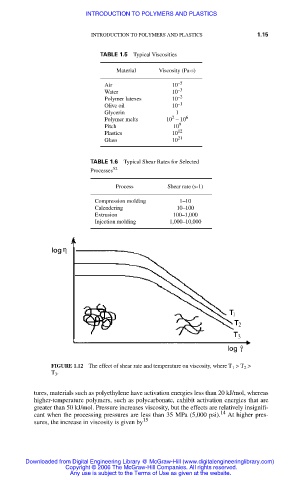
FIGURE 1.12 The effect of shear rate and temperature on viscosity, where T > T >
1
2
T .
3
tures, materials such as polyethylene have activation energies less than 20 kJ/mol, whereas
higher-temperature polymers, such as polycarbonate, exhibit activation energies that are
greater than 50 kJ/mol. Pressure increases viscosity, but the effects are relatively insignifi-
14
cant when the processing pressures are less than 35 MPa (5,000 psi). At higher pres-
15
sures, the increase in viscosity is given by
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.