Page 49 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 49
INTRODUCTION TO POLYMERS AND PLASTICS
INTRODUCTION TO POLYMERS AND PLASTICS 1.35
• Billow drape forming
• Billow vacuum forming
• Vacuum snap-back forming
• Plug assist vacuum forming
• Plug assist pressure forming
• Plug assist drape forming
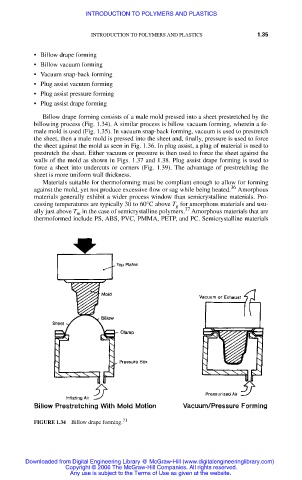
Billow drape forming consists of a male mold pressed into a sheet prestretched by the
billowing process (Fig. 1.34). A similar process is billow vacuum forming, wherein a fe-
male mold is used (Fig. 1.35). In vacuum snap-back forming, vacuum is used to prestretch
the sheet, then a male mold is pressed into the sheet and, finally, pressure is used to force
the sheet against the mold as seen in Fig. 1.36. In plug assist, a plug of material is used to
prestretch the sheet. Either vacuum or pressure is then used to force the sheet against the
walls of the mold as shown in Figs. 1.37 and 1.38. Plug assist drape forming is used to
force a sheet into undercuts or corners (Fig. 1.39). The advantage of prestretching the
sheet is more uniform wall thickness.
Materials suitable for thermoforming must be compliant enough to allow for forming
36
against the mold, yet not produce excessive flow or sag while being heated. Amorphous
materials generally exhibit a wider process window than semicrystalline materials. Pro-
cessing temperatures are typically 30 to 60°C above T for amorphous materials and usu-
g
37
ally just above T in the case of semicrystalline polymers. Amorphous materials that are
m
thermoformed include PS, ABS, PVC, PMMA, PETP, and PC. Semicrystalline materials
FIGURE 1.34 Billow drape forming. 71
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.