Page 58 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 58
Testing and characterization of fibers 39
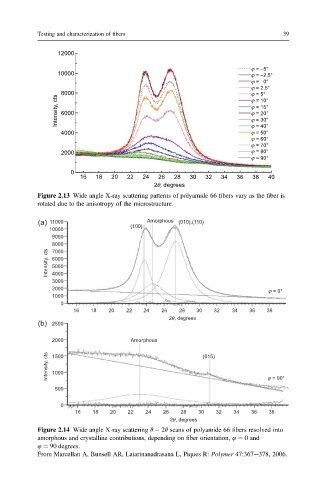
12000
ϕ = –5°
10000 ϕ = –2,5°
ϕ = 0°
ϕ = 2,5°
8000 ϕ = 5°
Intensity, cts 6000 ϕ = 15°
ϕ = 10°
ϕ = 20°
ϕ = 30°
4000 ϕ = 40°
ϕ = 50°
ϕ = 60°
ϕ = 70°
2000 ϕ = 80°
ϕ = 90°
0
16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40
2θ, degrees
Figure 2.13 Wide angle X-ray scattering patterns of polyamide 66 fibers vary as the fiber is
rotated due to the anisotropy of the microstructure.
(a) 11000 Amorphous (010),(110)
10000 (100)
9000
8000
Intensity, cts 6000
7000
5000
4000
3000
2000
ϕ = 0°
1000
0
16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38
2θ, degrees
(b) 2500
2000 Amorphous
Intensity, cts 1500 (015)
1000
500 ϕ = 90°
0
16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38
2θ, degrees
Figure 2.14 Wide angle X-ray scattering q 2q scans of polyamide 66 fibers resolved into
amorphous and crystalline contributions, depending on fiber orientation, 4 ¼ 0 and
4 ¼ 90 degrees.
From Marcellan A, Bunsell AR, Laiarinanadrasana L, Piques R: Polymer 47:367e378, 2006.