Page 97 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 97
78 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
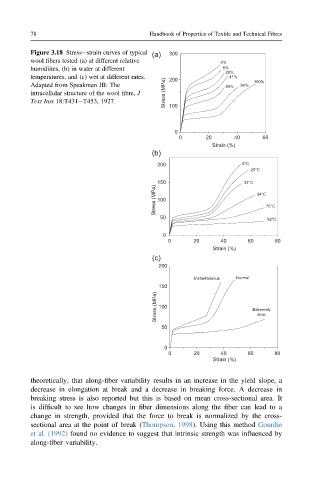
Figure 3.18 Stressestrain curves of typical (a) 300
wool fibers tested (a) at different relative 0%
humidities, (b) in water at different 8%
28%
temperatures, and (c) wet at different rates. 200 41% 100%
Adapted from Speakman JB: The 58% 84%
intracellular structure of the wool fibre, J Stress (MPa)
Text Inst 18:T431eT453, 1927. 100
0
0 20 40 60
Strain (%)
(b)
200 0°C
25°C
150 33°C
Stress (MPa) 100 64°C 75°C
50 92°C
0
0 20 40 60 80
Strain (%)
(c)
200
Instantaneous Normal
150
Stress (MPa) 100 Extremely
slow
50
0
0 20 40 60 80
Strain (%)
theoretically, that along-fiber variability results in an increase in the yield slope, a
decrease in elongation at break and a decrease in breaking force. A decrease in
breaking stress is also reported but this is based on mean cross-sectional area. It
is difficult to see how changes in fiber dimensions along the fiber can lead to a
change in strength, provided that the force to break is normalized by the cross-
sectional area at the point of break (Thompson, 1998). Using this method Gourdie
et al. (1992) found no evidence to suggest that intrinsic strength was influenced by
along-fiber variability.