Page 18 - Handbook of Structural Steel Connection Design and Details
P. 18
Fasteners and Welds for Structural Connections
Fasteners and Welds for Structural Connections 3
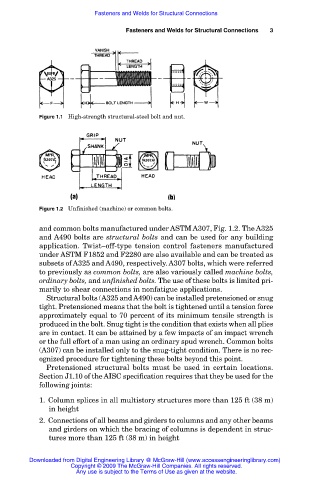
Figure 1.1 High-strength structural-steel bolt and nut.
Figure 1.2 Unfinished (machine) or common bolts.
and common bolts manufactured under ASTM A307, Fig. 1.2. The A325
and A490 bolts are structural bolts and can be used for any building
application. Twist–off-type tension control fasteners manufactured
under ASTM F1852 and F2280 are also available and can be treated as
subsets of A325 and A490, respectively. A307 bolts, which were referred
to previously as common bolts, are also variously called machine bolts,
ordinary bolts, and unfinished bolts. The use of these bolts is limited pri-
marily to shear connections in nonfatigue applications.
Structural bolts (A325 and A490) can be installed pretensioned or snug
tight. Pretensioned means that the bolt is tightened until a tension force
approximately equal to 70 percent of its minimum tensile strength is
produced in the bolt. Snug tight is the condition that exists when all plies
are in contact. It can be attained by a few impacts of an impact wrench
or the full effort of a man using an ordinary spud wrench. Common bolts
(A307) can be installed only to the snug-tight condition. There is no rec-
ognized procedure for tightening these bolts beyond this point.
Pretensioned structural bolts must be used in certain locations.
Section J1.10 of the AISC specification requires that they be used for the
following joints:
1. Column splices in all multistory structures more than 125 ft (38 m)
in height
2. Connections of all beams and girders to columns and any other beams
and girders on which the bracing of columns is dependent in struc-
tures more than 125 ft (38 m) in height
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.