Page 20 - Handbook of Structural Steel Connection Design and Details
P. 20
Fasteners and Welds for Structural Connections
Fasteners and Welds for Structural Connections 5
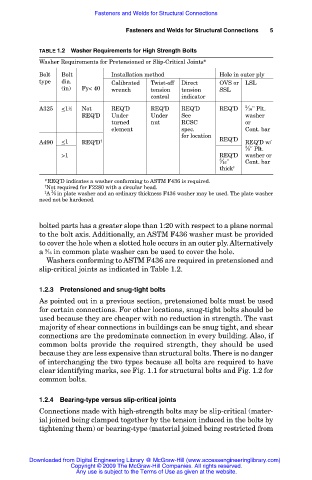
TABLE 1.2 Washer Requirements for High Strength Bolts
Washer Requirements for Pretensioned or Slip-Critical Joints*
Bolt Bolt Installation method Hole in outer ply
type dia. Calibrated Twist-off Direct OVS or LSL
(in) Fy< 40 wrench tension tension SSL
control indicator
A325 <1 ⁄2 Not REQ’D REQ’D REQ’D REQ’D 5 ⁄16'' Plt.
1
REQ’D Under Under See washer
turned nut RCSC or
element spec. Cont. bar
for location
A490 <1 REQ’D † REQ’D REQ’D w/
3 ⁄8'' Plt.
>1 REQ’D washer or
5 ⁄16'' Cont. bar
thick ‡
*REQ’D indicates a washer conforming to ASTM F436 is required.
† Not required for F2280 with a circular head.
3
‡ A ⁄8 in plate washer and an ordinary thickness F436 washer may be used. The plate washer
need not be hardened.
bolted parts has a greater slope than 1:20 with respect to a plane normal
to the bolt axis. Additionally, an ASTM F436 washer must be provided
to cover the hole when a slotted hole occurs in an outer ply. Alternatively
5
a ⁄16 in common plate washer can be used to cover the hole.
Washers conforming to ASTM F436 are required in pretensioned and
slip-critical joints as indicated in Table 1.2.
1.2.3 Pretensioned and snug-tight bolts
As pointed out in a previous section, pretensioned bolts must be used
for certain connections. For other locations, snug-tight bolts should be
used because they are cheaper with no reduction in strength. The vast
majority of shear connections in buildings can be snug tight, and shear
connections are the predominate connection in every building. Also, if
common bolts provide the required strength, they should be used
because they are less expensive than structural bolts. There is no danger
of interchanging the two types because all bolts are required to have
clear identifying marks, see Fig. 1.1 for structural bolts and Fig. 1.2 for
common bolts.
1.2.4 Bearing-type versus slip-critical joints
Connections made with high-strength bolts may be slip-critical (mater-
ial joined being clamped together by the tension induced in the bolts by
tightening them) or bearing-type (material joined being restricted from
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.