Page 147 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 147
142 Water Repelling (Hydrophobization)
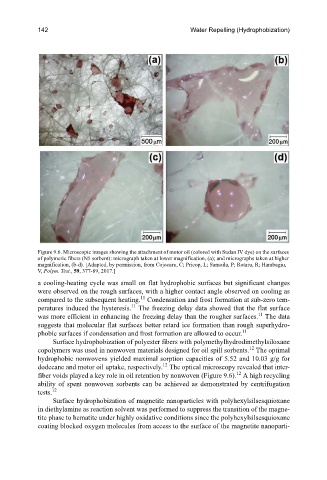
Figure 9.6. Microscopic images showing the attachment of motor oil (colored with Sudan IV dye) on the surfaces
of polymeric fibers (N5 sorbent): micrograph taken at lower magnification, (a); and micrographs taken at higher
magnification, (b-d). [Adapted, by permission, from Cojocaru, C; Pricop, L; Samoila, P; Rotaru, R; Harabagiu,
V, Polym. Test., 59, 377-89, 2017.]
a cooling-heating cycle was small on flat hydrophobic surfaces but significant changes
were observed on the rough surfaces, with a higher contact angle observed on cooling as
11
compared to the subsequent heating. Condensation and frost formation at sub-zero tem-
11
peratures induced the hysteresis. The freezing delay data showed that the flat surface
11
was more efficient in enhancing the freezing delay than the rougher surfaces. The data
suggests that molecular flat surfaces better retard ice formation than rough superhydro-
11
phobic surfaces if condensation and frost formation are allowed to occur.
Surface hydrophobization of polyester fibers with polymethylhydrodimethylsiloxane
12
copolymers was used in nonwoven materials designed for oil spill sorbents. The optimal
hydrophobic nonwovens yielded maximal sorption capacities of 5.52 and 10.03 g/g for
12
dodecane and motor oil uptake, respectively. The optical microscopy revealed that inter-
12
fiber voids played a key role in oil retention by nonwoven (Figure 9.6). A high recycling
ability of spent nonwoven sorbents can be achieved as demonstrated by centrifugation
12
tests.
Surface hydrophobization of magnetite nanoparticles with polyhexylsilsesquioxane
in diethylamine as reaction solvent was performed to suppress the transition of the magne-
tite phase to hematite under highly oxidative conditions since the polyhexylsilsesquioxane
coating blocked oxygen molecules from access to the surface of the magnetite nanoparti-