Page 150 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 150
9.1 Methods and mechanisms of hydrophobization 145
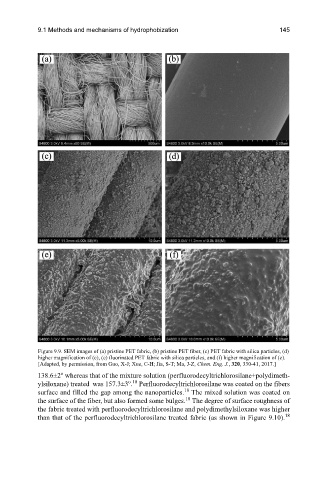
Figure 9.9. SEM images of (a) pristine PET fabric, (b) pristine PET fiber, (c) PET fabric with silica particles, (d)
higher magnification of (c), (e) fluorinated PET fabric with silica particles, and (f) higher magnification of (e).
[Adapted, by permission, from Guo, X-J; Xue, C-H; Jia, S-T; Ma, J-Z, Chem. Eng. J., 320, 330-41, 2017.]
o
138.6±2 whereas that of the mixture solution (perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane+polydimeth-
o 18
ylsiloxane) treated was 157.3±3 . Perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane was coated on the fibers
18
surface and filled the gap among the nanoparticles. The mixed solution was coated on
18
the surface of the fiber, but also formed some bulges. The degree of surface roughness of
the fabric treated with perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane and polydimethylsiloxane was higher
than that of the perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane treated fabric (as shown in Figure 9.10). 18