Page 179 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 179
174 The Coefficient of Friction
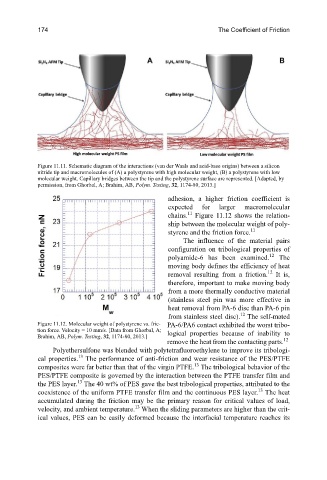
Figure 11.11. Schematic diagram of the interactions (van der Waals and acid-base origins) between a silicon
nitride tip and macromolecules of (A) a polystyrene with high molecular weight, (B) a polystyrene with low
molecular weight. Capillary bridges between the tip and the polystyrene surface are represented. [Adapted, by
permission, from Ghorbal, A; Brahim, AB, Polym. Testing, 32, 1174-80, 2013.]
adhesion, a higher friction coefficient is
expected for larger macromolecular
11
chains. Figure 11.12 shows the relation-
ship between the molecular weight of poly-
11
styrene and the friction force.
The influence of the material pairs
configuration on tribological properties of
12
polyamide-6 has been examined. The
moving body defines the efficiency of heat
12
removal resulting from a friction. It is,
therefore, important to make moving body
from a more thermally conductive material
(stainless steel pin was more effective in
heat removal from PA-6 disc than PA-6 pin
12
from stainless steel disc). The self-mated
Figure 11.12. Molecular weight of polystyrene vs. fric- PA-6/PA6 contact exhibited the worst tribo-
tion force. Velocity = 10 mm/s. [Data from Ghorbal, A; logical properties because of inability to
Brahim, AB, Polym. Testing, 32, 1174-80, 2013.]
12
remove the heat from the contacting parts.
Polyethersulfone was blended with polytetrafluoroethylene to improve its tribologi-
13
cal properties. The performance of anti-friction and wear resistance of the PES/PTFE
13
composites were far better than that of the virgin PTFE. The tribological behavior of the
PES/PTFE composite is governed by the interaction between the PTFE transfer film and
13
the PES layer. The 40 wt% of PES gave the best tribological properties, attributed to the
13
coexistence of the uniform PTFE transfer film and the continuous PES layer. The heat
accumulated during the friction may be the primary reason for critical values of load,
13
velocity, and ambient temperature. When the sliding parameters are higher than the crit-
ical values, PES can be easily deformed because the interfacial temperature reaches its