Page 114 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 114
Operations over GF ( p ) 97
x are k-bit naturals, − 2 2k − 1 ≤ u(i) < 2 2k − 1 , so that c and d are 2k-bit 2’s-
complement integers. For computing z = c − dq, where q is a k-bit
natural, a slightly modified version of the right-to-left multiplication
algorithm can be used:
0
c − dq = c − d(q · 2 k − 1 + q · 2 k − 2 + . . . + q · 2 )
k − 1 k − 2 0
−
= [((((c − q d)2 − 1 − q d)2 − 1 . . . )2 − 1 − q d)2 ]2 (4.17)
− 1
k
0 1 k − 1
Algorithm 4.3—Subtract and shift algorithm
w := c;
for i in 0 .. k-1 loop w := (w - q(i)*d)/2; end loop;
z := w*(2**k);
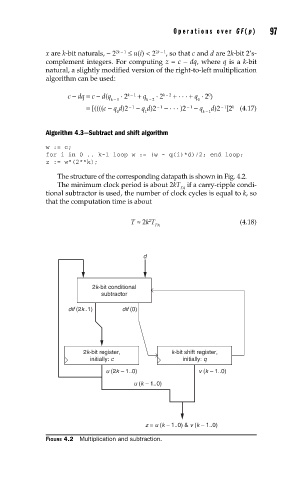
The structure of the corresponding datapath is shown in Fig. 4.2.
The minimum clock period is about 2kT if a carry-ripple condi-
FA
tional subtractor is used, the number of clock cycles is equal to k, so
that the computation time is about
T ≈ 2k T (4.18)
2
FA
d
2k-bit conditional
subtractor
dif (2k..1) dif (0)
2k-bit register, k-bit shift register,
initially: c initially: q
u (2k – 1..0) v (k – 1..0)
u (k – 1..0)
z = u (k – 1..0) & v (k – 1..0)
FIGURE 4.2 Multiplication and subtraction.