Page 119 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 119
102 Cha pte r F o u r
end loop;
if b >= a then b := b-a; d := (d-c) mod P;
else
Old_b := b; b := a-b; a := Old_b;
Old_d := d; d := (c-d) mod P; c := Old_d;
end if;
end loop;
Z := c;
An executable Ada file binary_algorithm.adb, including Algo-
rithm 4.4, is available at www.arithmetic-circuits.org.
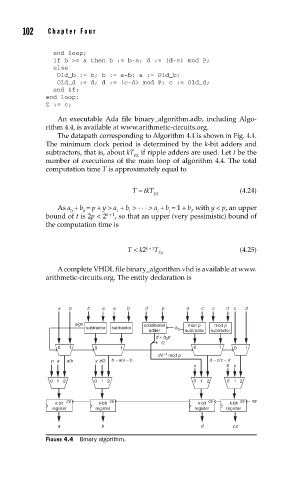
The datapath corresponding to Algorithm 4.4 is shown in Fig. 4.4.
The minimum clock period is determined by the k-bit adders and
subtractors, that is, about kT if ripple adders are used. Let t be the
FA
number of executions of the main loop of algorithm 4.4. The total
computation time T is approximately equal to
T ≈ tkT (4.24)
FA
As a + b = p + y > a + b > . . . > a + b = 1 + b , with y < p, an upper
0 0 1 1 i i i
bound of t is 2p < 2 k + 1 , so that an upper (very pessimistic) bound of
the computation time is
T < k2 k + 1 T (4.25)
FA
A complete VHDL file binary_algorithm.vhd is available at www.
arithmetic-circuits.org. The entity declaration is
a b b a a b d p d c c d c d
sign conditional mod p mod p
subtractor subtractor b
adder 0 subtractor subtractor
d + b p
0
/2
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
–1
d2 mod p
pa a/b yb/2 b – a/a – b d – c/c – d
x 0 c
01 2 01 2 01 2 01 2
ce ce ce ce ce
k-bit k-bit k-bit k-bit
register register register register
a b d z,c
FIGURE 4.4 Binary algorithm.