Page 124 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 124
Operations over GF ( p ) 107
b := (b-a)/4; d := divide_by_4(d-c, p);
end if;
if dif < 0 then a := old_b; c := old_d; dif := -dif - 1;
elsif dif = 0 then dif := dif - 1; min := min - 1;
else dif := dif - 1;
end if;
end if;
end loop;
if c < 0 then c := c + p; end if;
if a = 1 then z := c; else z := p-c; end if;
Executable Ada files plus_minus_algorithm.adb and plus_minus_
algorithm2.adb, including Algorithms 4.5 and 4.6, are available at
www.arithmetic-circuits.org.
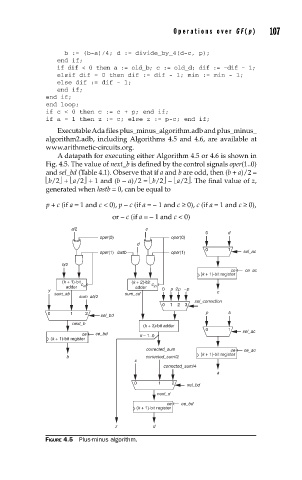
A datapath for executing either Algorithm 4.5 or 4.6 is shown in
Fig. 4.5. The value of next_b is defined by the control signals oper(1..0)
and sel_bd (Table 4.1). Observe that if a and b are odd, then (b + a)/2 =
⎣b/2⎦+ ⎣a/2⎦+ 1 and (b − a)/2 =⎣b/2⎦− ⎣a/2⎦. The final value of z,
generated when lastb = 0, can be equal to
p + c (if a = 1 and c < 0), p − c (if a =− 1 and c ≥ 0), c (if a = 1 and c ≥ 0),
or − c (if a =− 1 and c < 0)
a/2 c
0 d
oper(0) oper(0)
d
0 1
oper(1) lastb oper(1) sel_ac
b/2
ce ce_ac
(k + 1)-bit register
(k + 1)-bit (k + 2)-bit
adder c in adder c in
y 0 p 2p –p c
sum_ab sum_cd
sum_ab/2
sel_correction
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 sel_bd p b
next_b
(k + 3)-bit adder
0 1 sel_ac
ce ce_bd k – 1..0
(k + 1)-bit register
corrected_sum ce ce_ac
(k + 1)-bit register
b corrected_sum/2
x
corrected_sum/4
a
0 1 2
sel_bd
next_d
ce ce_bd
(k + 1)-bit register
z d
FIGURE 4.5 Plus-minus algorithm.