Page 271 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 271
m
Operations over GF (2 )—Normal Bases 251
E (m – 1 : 0) A (m – 1 : 0)
sq_c (m – 1 : 0)
1 0 inic
inic
m-bit shift register m-bit register
shift_right
ee 0
cc (m – 1 : 0)
bb cc
cc m–1 cc m–2 cc m–3 cc 0
. . .
NB_multiplier . . .
sq_c m–1 sq_c m–2 sq_c 1 sq_c 0
NB_squarer
mult_bc (m – 1 : 0)
ee 0
inic
m-bit register
ce_c
bb (m – 1 : 0)
B (m – 1 : 0)
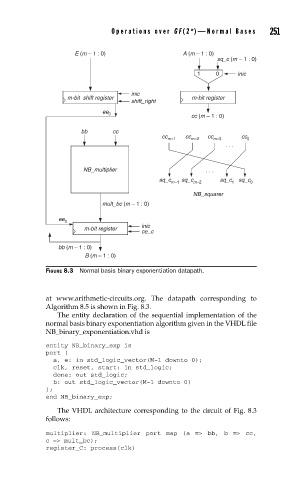
FIGURE 8.3 Normal basis binary exponentiation datapath.
at www.arithmetic-circuits.org. The datapath corresponding to
Algorithm 8.5 is shown in Fig. 8.3.
The entity declaration of the sequential implementation of the
normal basis binary exponentiation algorithm given in the VHDL file
NB_binary_exponentiation.vhd is
entity NB_binary_exp is
port (
a, e: in std_logic_vector(M-1 downto 0);
clk, reset, start: in std_logic;
done: out std_logic;
b: out std_logic_vector(M-1 downto 0)
);
end NB_binary_exp;
The VHDL architecture corresponding to the circuit of Fig. 8.3
follows:
multiplier: NB_multiplier port map (a => bb, b => cc,
c => mult_bc);
register_C: process(clk)