Page 34 - High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Fundamentals, Design and Applications
P. 34
Introduction to SOPCs 15
Originally, SOFCs were designed to compete with large power generation units
like central power stations, ships and locomotives, especially to run on coal gas
or heavy fuels. During the last 10 years, the realisation has steadily dawned that
SOFCs can work well in small, portable, residential and auxiliary power systems,
particularly running on natural gas, propane or biogas [34]. Typical examples of
such developments are those of Sulzer [29], AdePan, Delphi, General Electric and
Siemens Westinghouse.
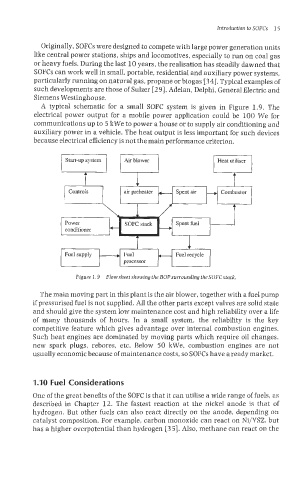
A typical schematic for a small SOFC system is given in Figure 1.9. The
electrical power output for a mobile power application could be 100 We for
communications up to 5 kWe to power a house or to supply air conditioning and
auxiliary power in a vehicle. The heat output is less important for such devices
because electrical efficiency is not the main performance criterion.
Start-up system pziq
ti P
Heat utiliser
Figure 1.9 Flow sheet showingthe BOPsurrounding theSOFCstack.
The main moving part in this plant is the air blower, together with a fuel pump
il pressurised fuel is not supplied. All the other parts except valves are solid state
and should give the system low maintenance cost and high reliability over a life
of many thousands of hours. In a small system, the reliability is the key
competitive feature which gives advantage over internal combustion engines.
Such heat engines are dominated by moving parts which require oil changes,
new spark plugs, rebores, etc. Below 50 kWe, combustion engines are not
usually economic because of maintenance costs, so SOFCs have a ready market.
Fuel Considerations
One of the great benefits of the SOFC is that it can utilise a wide range of fuels, as
described in Chapter 12. The fastest reaction at the nickel anode is that of
hydrogen. But other fuels can also react directly on the anode, depending on
catalyst composition. For example, carbon monoxide can react on Ni/YSZ, but
has a higher overpotential than hydrogen [35]. Also, methane can react on the