Page 100 - Highway Engineering Handbook Building and Rehabilitating the Infrastructure
P. 100
HIGHWAY LOCATION, DESIGN, AND TRAFFIC 83
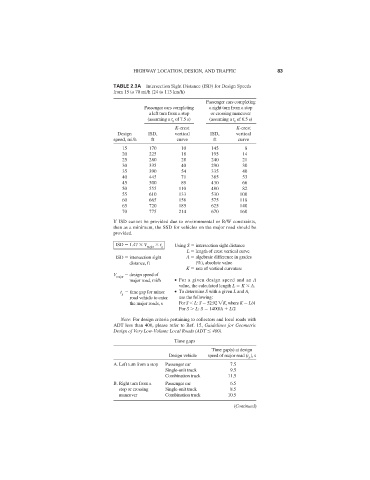
TABLE 2.3A Intersection Sight Distance (ISD) for Design Speeds
from 15 to 70 mi/h (24 to 113 km/h)
Passenger cars completing
Passenger cars completing a right turn from a stop
a left turn from a stop or crossing maneuver
(assuming a t g of 7.5 s) (assuming a t g of 6.5 s)
K-crest K-crest
Design ISD, vertical ISD, vertical
speed, mi/h ft curve ft curve
15 170 10 145 8
20 225 18 195 14
25 280 28 240 21
30 335 40 290 30
35 390 54 335 40
40 445 71 385 53
45 500 89 430 66
50 555 110 480 82
55 610 133 530 100
60 665 158 575 118
65 720 185 625 140
70 775 214 670 160
If ISD cannot be provided due to environmental or R/W constraints,
then as a minimum, the SSD for vehicles on the major road should be
provided.
ISD 1.47 V t Using S intersection sight distance
major g
L length of crest vertical curve
ISD intersection sight A algebraic difference in grades
distance, ft (%), absolute value
K rate of vertical curvature
V design speed of
major
major road, mi/h ● For a given design speed and an A
value, the calculated length L K A.
t time gap for minor ● To determine S with a given L and A,
g
road vehicle to enter use the following:
the major roads, s For S L: S 52.92 K , where K L/A
For S L: S 1400/A L/2
Note: For design criteria pertaining to collectors and local roads with
ADT less than 400, please refer to Ref. 15, Guidelines for Geometric
Design of Very Low-Volume Local Roads (ADT 400).
Time gaps
Time gap(s) at design
Design vehicle speed of major road (t g ),s
A. Left turn from a stop Passenger car 7.5
Single-unit truck 9.5
Combination truck 11.5
B. Right turn from a Passenger car 6.5
stop or crossing Single-unit truck 8.5
maneuver Combination truck 10.5
(Continued)