Page 99 - Highway Engineering Handbook Building and Rehabilitating the Infrastructure
P. 99
82 CHAPTER TWO
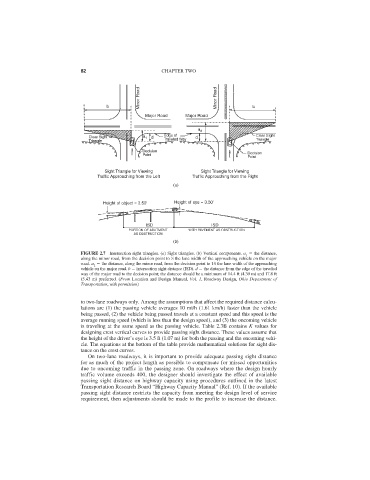
FIGURE 2.7 Intersection sight triangles. (a) Sight triangles. (b) Vertical components. a the distance,
1
1
along the minor road, from the decision point to ⁄2 the lane width of the approaching vehicle on the major
1
road. a the distance, along the minor road, from the decision point to 1 ⁄2 the lane width of the approaching
2
vehicle on the major road. b intersection sight distance (ISD). d the distance from the edge of the traveled
way of the major road to the decision point; the distance should be a minimum of 14.4 ft (4.39 m) and 17.8 ft
(5.43 m) preferred. (From Location and Design Manual, Vol. 1, Roadway Design, Ohio Department of
Transportation, with permission)
to two-lane roadways only. Among the assumptions that affect the required distance calcu-
lations are (1) the passing vehicle averages 10 mi/h (1.61 km/h) faster than the vehicle
being passed, (2) the vehicle being passed travels at a constant speed and this speed is the
average running speed (which is less than the design speed), and (3) the oncoming vehicle
is traveling at the same speed as the passing vehicle. Table 2.3B contains K values for
designing crest vertical curves to provide passing sight distance. These values assume that
the height of the driver’s eye is 3.5 ft (1.07 m) for both the passing and the oncoming vehi-
cle. The equations at the bottom of the table provide mathematical solutions for sight dis-
tance on the crest curves.
On two-lane roadways, it is important to provide adequate passing sight distance
for as much of the project length as possible to compensate for missed opportunities
due to oncoming traffic in the passing zone. On roadways where the design hourly
traffic volume exceeds 400, the designer should investigate the effect of available
passing sight distance on highway capacity using procedures outlined in the latest
Transportation Research Board “Highway Capacity Manual” (Ref. 10). If the available
passing sight distance restricts the capacity from meeting the design level of service
requirement, then adjustments should be made to the profile to increase the distance.