Page 138 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 138
130 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
10000
4000
2000
1000
500
300
200
100
60
40
30
20
10
8
7
6
5 4 B
Viscosity (cSt) 3 2
1 F
0.9 C
0.8 G
0.7
0.6 A
D
0.5
E
0.4
0.3 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 170 190 210 230 250 270 290 310 330 350 370 390
Temperature(°C)
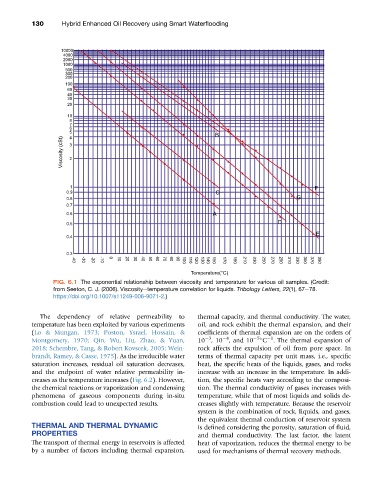
FIG. 6.1 The exponential relationship between viscosity and temperature for various oil samples. (Credit:
from Seeton, C. J. (2006). Viscosityetemperature correlation for liquids. Tribology Letters, 22(1), 67e78.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-006-9071-2.)
The dependency of relative permeability to thermal capacity, and thermal conductivity. The water,
temperature has been exploited by various experiments oil, and rock exhibit the thermal expansion, and their
(Lo & Mungan, 1973; Poston, Ysrael, Hossain, & coefficients of thermal expansion are on the orders of
3
1
4
Montgomery, 1970; Qin, Wu, Liu, Zhao, & Yuan, 10 ,10 , and 10 5 C . The thermal expansion of
2018; Schembre, Tang, & Robert Kovscek, 2005; Wein- rock affects the expulsion of oil from pore space. In
brandt, Ramey, & Casse, 1975). As the irreducible water terms of thermal capacity per unit mass, i.e., specific
saturation increases, residual oil saturation decreases, heat, the specific heats of the liquids, gases, and rocks
and the endpoint of water relative permeability in- increase with an increase in the temperature. In addi-
creases as the temperature increases (Fig. 6.2). However, tion, the specific heats vary according to the composi-
the chemical reactions or vaporization and condensing tion. The thermal conductivity of gases increases with
phenomena of gaseous components during in-situ temperature, while that of most liquids and solids de-
combustion could lead to unexpected results. creases slightly with temperature. Because the reservoir
system is the combination of rock, liquids, and gases,
the equivalent thermal conduction of reservoir system
THERMAL AND THERMAL DYNAMIC is defined considering the porosity, saturation of fluid,
PROPERTIES and thermal conductivity. The last factor, the latent
The transport of thermal energy in reservoirs is affected heat of vaporization, reduces the thermal energy to be
by a number of factors including thermal expansion, used for mechanisms of thermal recovery methods.