Page 205 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 205
192 Identifying and Quantifying Sources of Uncertainty
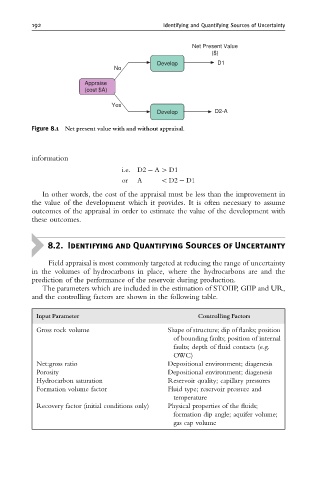
Net Present Value
($)
Develop D1
No
Appraise
(cost $A)
Yes
Develop D2-A
Figure 8.1 Net present value with and without appraisal.
information
i:e: D2 A 4 D1
or A o D2 D1
In other words, the cost of the appraisal must be less than the improvement in
the value of the development which it provides. It is often necessary to assume
outcomes of the appraisal in order to estimate the value of the development with
these outcomes.
8.2. Identifying and Quantifying Sources of Uncertainty
Field appraisal is most commonly targeted at reducing the range of uncertainty
in the volumes of hydrocarbons in place, where the hydrocarbons are and the
prediction of the performance of the reservoir during production.
The parameters which are included in the estimation of STOIIP, GIIP and UR,
and the controlling factors are shown in the following table.
Input Parameter Controlling Factors
Gross rock volume Shape of structure; dip of flanks; position
of bounding faults; position of internal
faults; depth of fluid contacts (e.g.
OWC)
Net:gross ratio Depositional environment; diagenesis
Porosity Depositional environment; diagenesis
Hydrocarbon saturation Reservoir quality; capillary pressures
Formation volume factor Fluid type; reservoir pressure and
temperature
Recovery factor (initial conditions only) Physical properties of the fluids;
formation dip angle; aquifer volume;
gas cap volume