Page 209 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 209
196 Cost-Benefit Calculations for Appraisal
OWC
OWC OWC
A A A
OWC
low case medium case high case
100
cum.
p(x)%
well A oil bearing
50
well A dry
pre-appraisal
0
0 100 200 300 400
STOIIP (MMstb)
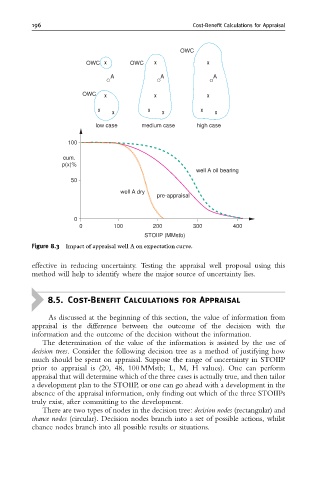
Figure 8.3 Impact of appraisal well A on expectation curve.
effective in reducing uncertainty. Testing the appraisal well proposal using this
method will help to identify where the major source of uncertainty lies.
8.5. Cost-Benefit Calculations for Appraisal
As discussed at the beginning of this section, the value of information from
appraisal is the difference between the outcome of the decision with the
information and the outcome of the decision without the information.
The determination of the value of the information is assisted by the use of
decision trees. Consider the following decision tree as a method of justifying how
much should be spent on appraisal. Suppose the range of uncertainty in STOIIP
prior to appraisal is (20, 48, 100 MMstb; L, M, H values). One can perform
appraisal that will determine which of the three cases is actually true, and then tailor
a development plan to the STOIIP, or one can go ahead with a development in the
absence of the appraisal information, only finding out which of the three STOIIPs
truly exist, after committing to the development.
There are two types of nodes in the decision tree: decision nodes (rectangular) and
chance nodes (circular). Decision nodes branch into a set of possible actions, whilst
chance nodes branch into all possible results or situations.