Page 286 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 286
Surface Facilities 273
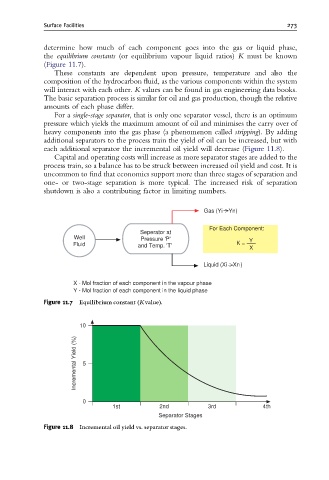
determine how much of each component goes into the gas or liquid phase,
the equilibrium constants (or equilibrium vapour liquid ratios) K must be known
(Figure 11.7).
These constants are dependent upon pressure, temperature and also the
composition of the hydrocarbon fluid, as the various components within the system
will interact with each other. K values can be found in gas engineering data books.
The basic separation process is similar for oil and gas production, though the relative
amounts of each phase differ.
For a single-stage separator, that is only one separator vessel, there is an optimum
pressure which yields the maximum amount of oil and minimises the carry over of
heavy components into the gas phase (a phenomenon called stripping). By adding
additional separators to the process train the yield of oil can be increased, but with
each additional separator the incremental oil yield will decrease (Figure 11.8).
Capital and operating costs will increase as more separator stages are added to the
process train, so a balance has to be struck between increased oil yield and cost. It is
uncommon to find that economics support more than three stages of separation and
one- or two-stage separation is more typical. The increased risk of separation
shutdown is also a contributing factor in limiting numbers.
Gas (Yi )
Yn
For Each Component:
Seperator at
Well Pressure 'P' Y
Fluid and Temp. 'T' K = X
Liquid (Xi )
Xn
X - Mol fraction of each component in the vapour phase
Y - Mol fraction of each component in the liquid phase
Figure 11.7 Equilibrium constant (Kvalue).
10
Incremental Yield (%) 5
0
1st 2nd 3rd 4th
Separator Stages
Figure 11.8 Incremental oil yield vs. separator stages.