Page 399 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 399
386 Managing the Subsurface
16.1. Managing the Subsurface
16.1.1. The reservoir performance
At the development planning stage, a reservoir model will have been constructed and
used to determine the optimum method of recovering the hydrocarbons from the
reservoir. The criteria for the optimum solution will most likely have been based on
profitability and safety. The model is initially based on a limited data set, perhaps a
seismic survey, five exploration and appraisal wells, and will therefore be an approxi-
mation of the true description of the field. As development drilling and production
commence, further data is collected and used to update both the geological model
which comprises the description of the structure, environment of deposition, dia-
genesis and fluid distribution and the description of the reservoir under dynamic
conditions or the reservoir model.
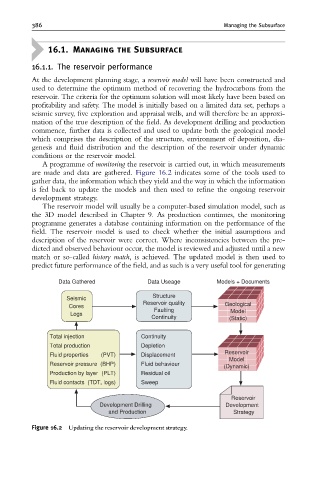
A programme of monitoring the reservoir is carried out, in which measurements
are made and data are gathered. Figure 16.2 indicates some of the tools used to
gather data, the information which they yield and the way in which the information
is fed back to update the models and then used to refine the ongoing reservoir
development strategy.
The reservoir model will usually be a computer-based simulation model, such as
the 3D model described in Chapter 9. As production continues, the monitoring
programme generates a database containing information on the performance of the
field. The reservoir model is used to check whether the initial assumptions and
description of the reservoir were correct. Where inconsistencies between the pre-
dicted and observed behaviour occur, the model is reviewed and adjusted until a new
match or so-called history match, is achieved. The updated model is then used to
predict future performance of the field, and as such is a very useful tool for generating
Data Gathered Data Useage Models + Documents
Structure
Seismic
Reservoir quality Geological
Cores
Faulting Model
Logs
Continuity (Static)
Total injection Continuity
Total production Depletion
Reservoir
Fluid properties (PVT) Displacement
Model
Reservoir pressure (BHP) Fluid behaviour
(Dynamic)
Production by layer (PLT) Residual oil
Fluid contacts (TDT, logs) Sweep
Reservoir
Development Drilling Development
and Production Strategy
Figure 16.2 Updating the reservoir development strategy.